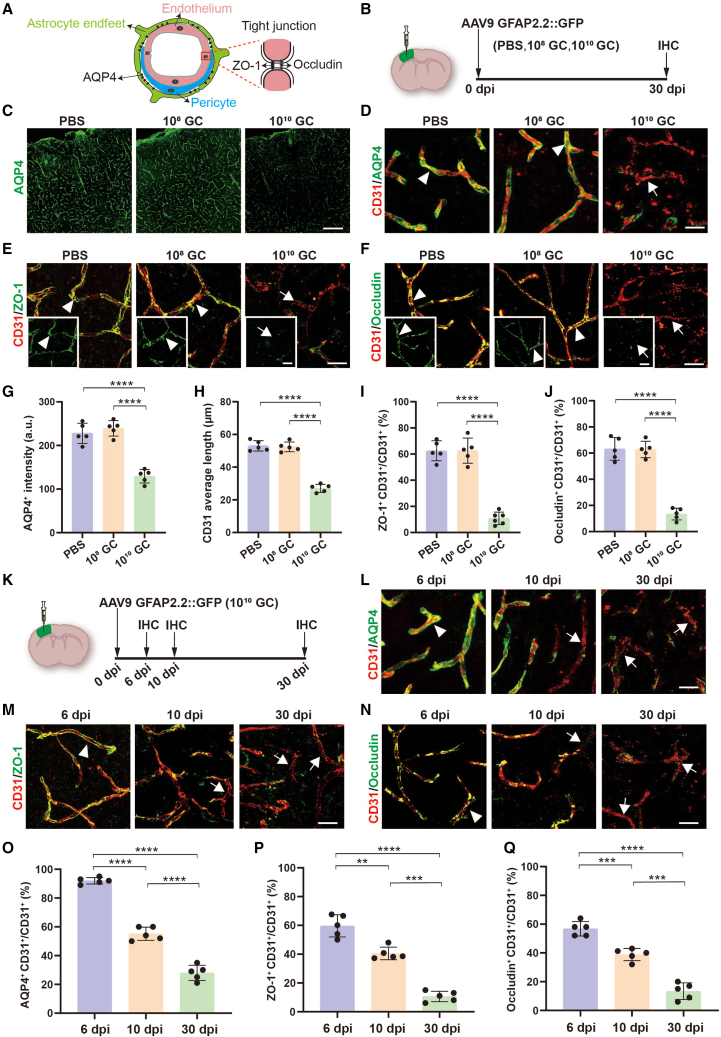
Figure 2.
High-titer AAV destroys BBB biological structures
(A) Diagram of BBB structure including astrocytic endfeet, pericytes, and tight junctions between endothelial cells. (B) Intracranial injection site, the serotype of AAV, and experimental timeline. (C) Representative low-magnification confocal images of focal areas of astrocytic endfeet (AQP4, green) in PBS and AAV injected regions, and robust AQP4 signals were lost in high-titer AAV treated mice. Scale bar, 200 μm. (D–F) High magnification confocal imaging of CD31 (endothelial cell marker, red) co-stained with AQP4 (D) (green), ZO-1 (E) (tight junction marker, green), and occludin (F) (tight junction marker, green) in PBS, 108 GC and 1010 GC groups. Arrowheads indicate endothelial cells that are wrapped by astrocytic endfeet (D) and sealed by ZO-1 (E) and occludin (F). Arrows indicate the endothelial cells that lost these structures after high-titer AAV injection. Scale bar, 20 μm. (G and H) Quantified data showing the intensity of AQP4 (G) and average length of CD31 (H) in different groups. (I and J) Quantified data showing the ratio of total ZO-1+ signals to total CD31+ signals (I) and the ratio of total occludin+ signals to total CD31+ signals (J) in different groups. These data reveal that the biological structure of the BBB is disrupted by high-titer AAVs. (K) Study design to examine effects of high-titer AAV injection into the cortex. (L–N) High-magnification confocal imaging of CD31 (endothelial cell marker; red) co-stained with AQP4 (L) (green), ZO-1 (M) (green), and occludin (N) (green) at 6, 10, and 30 dpi. Arrowheads indicate the typical BBB structure that contains astrocytic endfeet and tight junctions at 6 dpi after high-titer AAV injection. Arrow indicates the abnormal BBB that lost these signals starting at 10 dpi after high-titer AAV injection. Scale bars 20 μm. (O–Q) Quantified data showing the ratio of cerebral blood vessels that are surrounded by astrocytic endfeet (O), sealed by ZO-1 (P) and occludin (Q) at different time points after high-titer AAV injection. Values are shown as mean ± SD. n = 5 mice per group. One-way ANOVA analysis with Tukey test. Significance reported as ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.