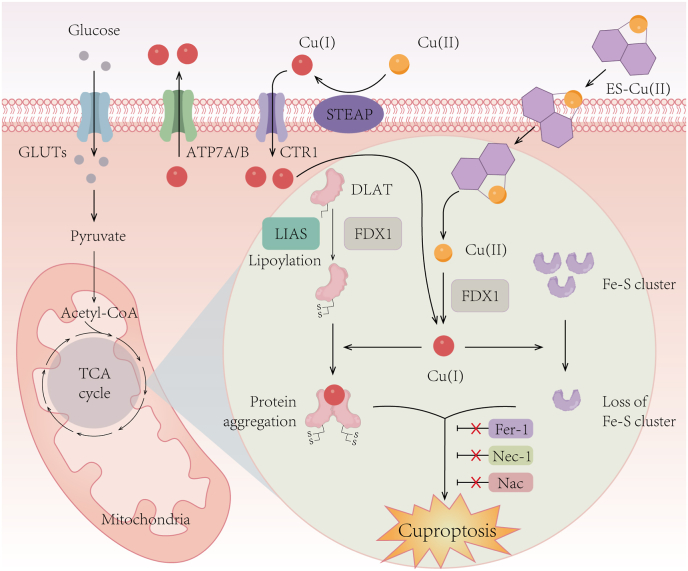
Fig. 5.
Schematic diagram of the mechanism of cuproptosis.
Elesclomol-induced cuproptosis primarily relies on its direct target FDX1, which catalyzes the reduction of Cu(II) to Cu(I). This reduction event facilitates the lipoylation and aggregation of enzymes, particularly DLAT, involving in the mitochondrial TCA cycle. Additionally, it triggers the loss of Fe–S cluster proteins. These aberrant processes collectively lead to proteotoxic stress and eventual cell death. Importantly, inhibitors targeting ferroptosis (Fer-1), necroptosis (Nec-1), and oxidative stress (NAC) do not affect the occurrence of cuproptosis. DLAT, dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase; LIAS, lipoic acid synthetase; Fer-1, ferrostatin-1; Nec-1, necrostatin-1; NAC, N-acetylcysteine.