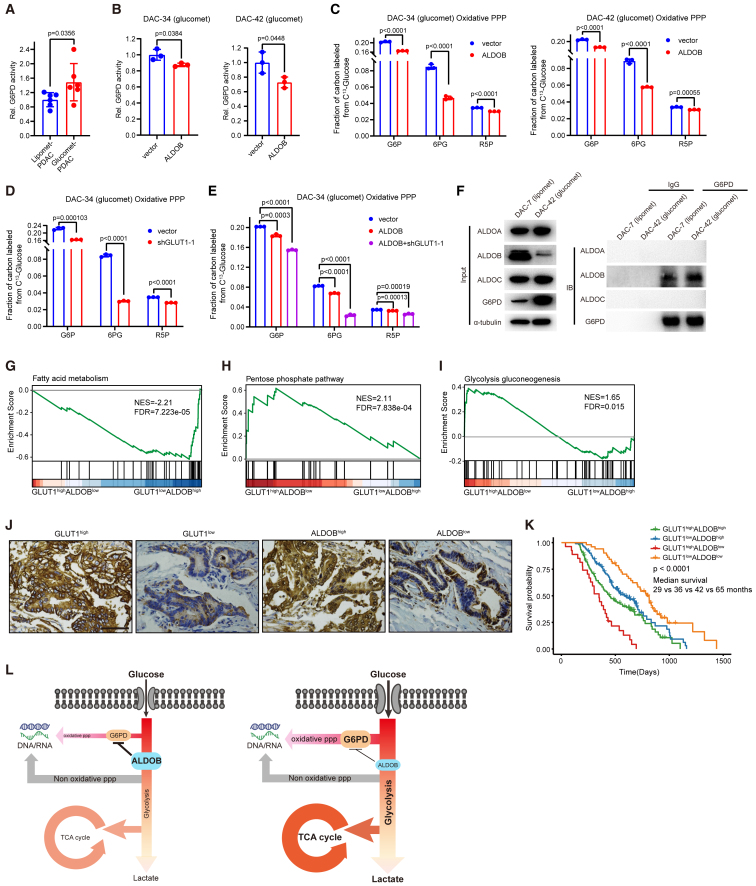
Figure 4.
The GLUT1/ALDOB/G6PD axis drives glucose metabolic reprogramming in glucomet-PDAC
(A) Relative G6PD enzyme activity in representative organoids of glucomet-PDAC (n = 6) and lipomet-PDAC (n = 6).
(B) Relative G6PD enzyme activity in vector- and ALDOB-overexpressing organoids (n = 3).
(C) Relative abundance of oxidative PPP metabolites in control and ALDOB-overexpressing organoids (n = 3).
(D and E) Relative abundance of oxidative PPP metabolites in control, GLUT1 knockdown, ALDOB overexpression, GLUT1 knockdown, and ALDOB overexpression organoids (n = 3).
(F) Endogenous ALDOB and G6PD interactions in PDAC organoids detected by immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments.
(G–I) TCGA patients with PDAC (n = 156) were divided into GLUT1high/ALDOBlow, GLUT1low/ALDOBhigh, and others based on GLUT1 and ALDOB expression levels. Samples with expression of GLUT1 in the top 40% and expression of ALDOB in the last 40% were named GLUT1high/ALDOBlow, while samples with expression of ALDOB in the top 40% and expression of GLUT1 in the last 40% were named GLUT1low/ALDOBhigh. GSEA enrichment plot for GLUT1high/ALDOBlow group versus GLUT1low/ALDOBhigh group of fatty acid metabolism (G), pentose phosphate pathway (H), and glycolysis/gluconeogenesis (I) signature genes.
(J) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining show high or low GLUT1 staining and high or low ALDOB staining in PDAC TMA (n = 285). Scale bar, 50 μm. Patients were divided into four groups based on ALDOB and GLUT1 expression levels: ALDOBhigh (++), ALDOB expression >50%; ALDOBlow (+), ALDOB expression <50%; GLUT1high (++), GLUT1 expression >50%; and GLUT1low (+), GLUT1 expression <50%.
(K) Kaplan-Meier survival curves based on the expression of GLUT1 and ALDOB in 285 patients with PDAC.
(L) Summary scheme highlighting the roles of the GLUT1/ALDOB/G6PD axis in glucose reprogramming.
Data are presented as the mean values ± SEMs, and statistical significance was computed by unpaired Student’s t test (A–E). Statistical significance was computed by log-rank test (K).