Figure 1.
Impact of high PPC on the number and quality of silkworm eggs
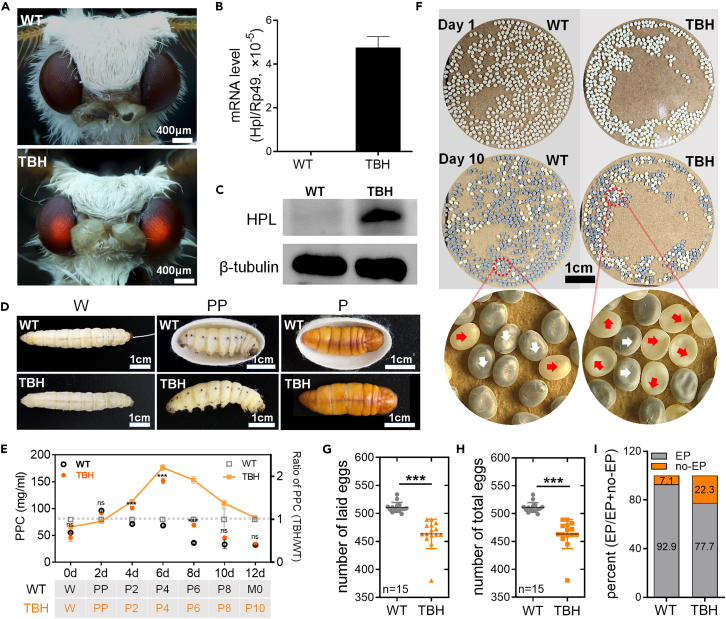
(A) Compound eyes of adults. The compound eyes showed red fluorescence due to the ERFP (Ds-Red) reporter gene in the transgenic mutant TBH.
(B) Transcription level of Hpl gene in the silk gland was detected by qRT-PCR. Rp49 was used as the internal reference gene. n = 3.
(C) Levels of HPL protein in the silk gland were analyzed by Western blotting. HPL protein is 68 kD, and the reference β-tubulin protein is 55 kD.
(D) Metamorphosis of TBH and WT. W, wandering stage, mature larvae begin to spin silk and form cocoons. PP, prepupal stage, the end of spinning and cocooning. P, pupal stage, complete larval-pupal metamorphosis development.
(E) PPC. P2-P10, pupa age 2 days–10 days. M0, newly molted adult stage. n = 3.
(F) Morphology of eggs. Day 1, just laid eggs; Day 10, eggs in the body pigmentation stage (EP), near hatching. The white arrow shows the eggs in EP and the red arrow shows eggs in the body no-pigmentation stage (no-EP).
(G) Number of laid eggs (n = 15).
(H) Total number of eggs (n = 15).
(I) EP rate (n = 6).
The data were mean ± SD, and the significance of the difference in the Student’s t test was ns, p > 0.05; ∗, p < 0.05; ∗∗, p < 0.01; ∗∗∗, p < 0.001.