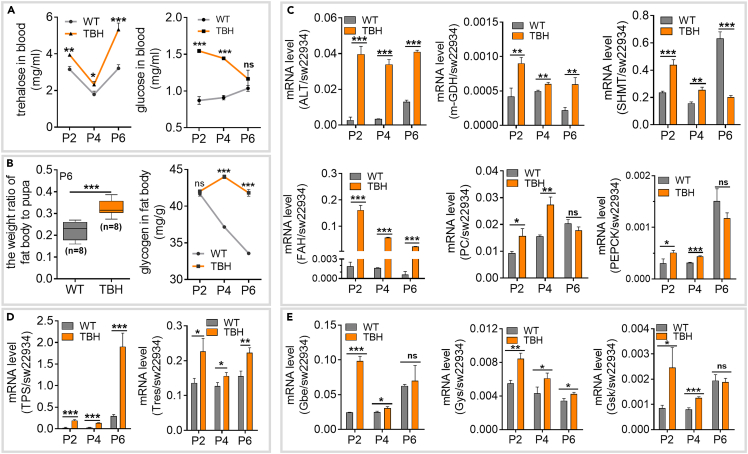
Figure 4.
High PPC induces hyperglycemia by activating the gluconeogenic pathway
(A) Trehalose and glucose levels in hemolymph (n = 3).
(B) Fat body index and glycogen content in the fat body (n = 3). Fat body index = fat body weight/pupa weight.
(C) Transcription levels of key genes of the gluconeogenesis pathway involved in the conversion of alanine, glycine, tyrosine, and serine were determined by qRT-PCR (n = 3). ALT, alanine aminotransferase gene; m-GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase gene; SHMT, serine hydroxymethyl transferase gene; FAH, fumarase gene; PC, pyruvate carboxylase gene; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene.
(D) Relative expression of genes related to trehalose synthesis (n = 3). TPS, trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene; Tres, trehalose synthetase gene.
(E) Transcriptional level of key genes for glycogen synthesis (n = 3). Gbe, glycogen branching enzyme gene; Gys, glycogen synthase gene; Gsk, glycogen synthase kinase gene. sw22934 was used as the reference gene for qRT-PCR.
The data were mean ± SD, and the significance of the difference in the Student’s t test was ns, p > 0.05; ∗, p < 0.05; ∗∗, p < 0.01; ∗∗∗, p < 0.001.