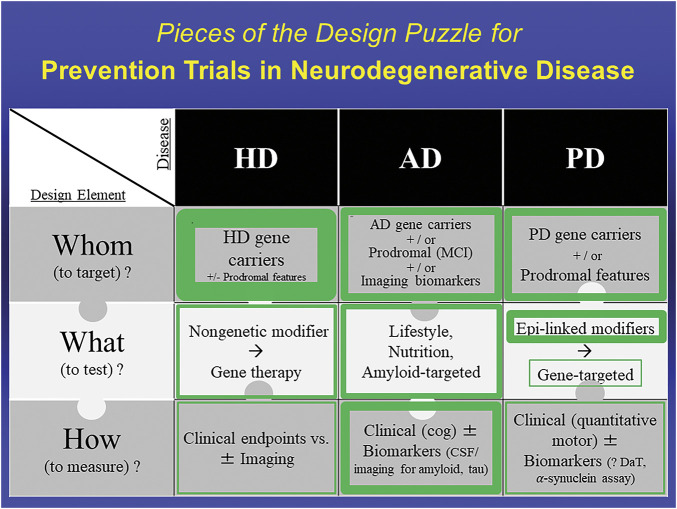
Figure 1. Pieces of the Design Puzzle for Prevention Trials in Neurodegenerative Disease: Comparing Early Progress in Selecting Design Elements for Prevention Trials Across HD, AD, and PD.
Thickness of green borders represents the relative extent to which the enclosed design element has been identified or established to enable initiation of prevention trials. For example, whom to target in HD is well established with the core feature of pathogenic expansion CAG repeats in the HD gene, possibly with prodromal features that increase likelihood of phenoconversion. In AD, all elements are sufficiently defined to have allowed numerous prevention trials. In PD, major advances in defining the genetics and prodromal state of PD have helped set the Whom piece of the trial design puzzle, and the relative safety and robustness of epidemiology (Epi)-linked risk modifiers compared to those in other neurodegenerative diseases have made them initially more attractive candidates for what to test, compared with emerging gene-targeted therapeutic strategies. How to measure prevention of PD before phenoconversion remains uncertain but is under intensive study. AD = Alzheimer disease; HD = Huntington disease; MCI = mild cognitive (cog) impairment; PD = Parkinson disease.