Figure 1.
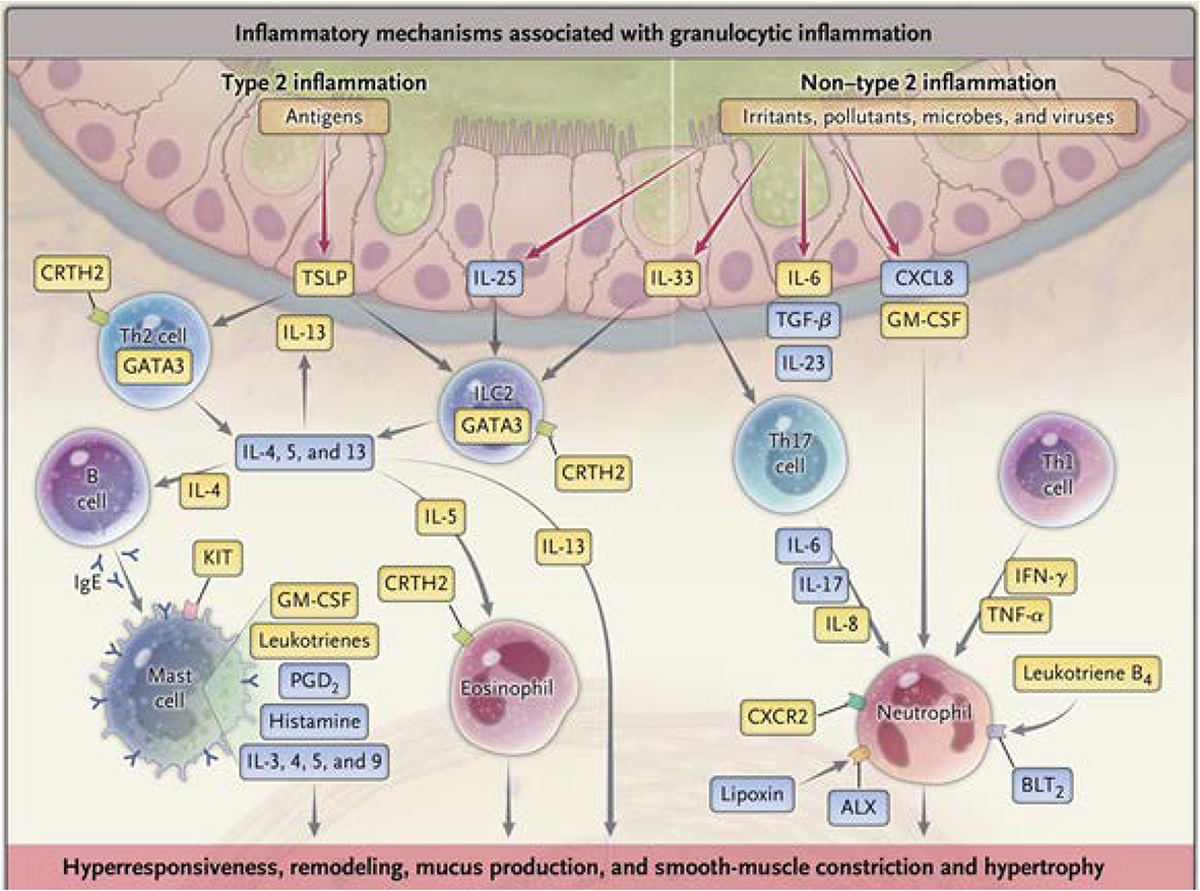
The inflammatory mechanisms that contribute to the pathophysiology of severe asthma are heterogeneous. ALX, lipoxin A4 receptor; BLT2, leukotriene B4 receptor 2; CRTH2, chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on Th2; CXCL8, CXC ligand 8; CXCR2. CXC chemokine receptor 2; GATA3, GATA binding protein 3; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN, Interferon; IL. interleukin; Ig. immunoglobulin; KIT, tyrosine kinase receptor; PGD2, prostaglandin D2; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; Th2, Type 2 helper; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin [89]. (Reprinted with permission).
