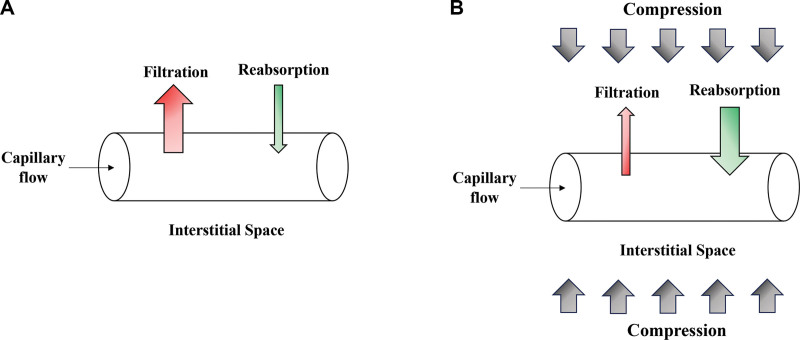
Fig. 1.
The effect of compression therapy on fluid accumulation in the interstitial space. The direction of fluid movement is determined by the balance of hydrostatic and oncotic forces exerted by both the intracapillary and interstitial spaces. A, The net result is initial fluid filtration out from the vessel into the interstitial space followed by fluid reabsorption. B, Applying compression therapy increases the hydrostatic forces, pushing fluid into the capillary, and leads to greater net absorption out of the interstitial space, thus decreasing clinical edema.