FIGURE 3.
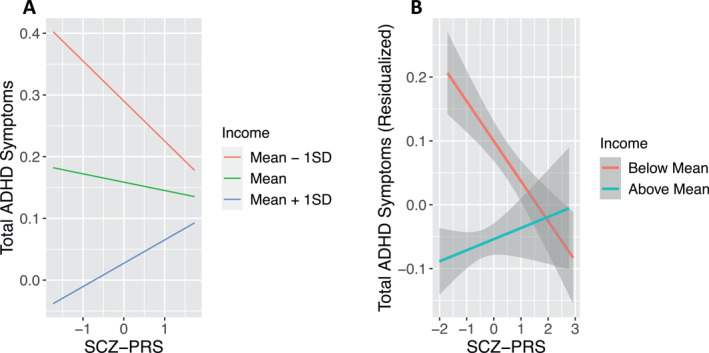
The interaction between SCZ PRS and family income is associated with total ADHD symptoms in the full ABCD cohort. Results indicate that symptoms vary depending on income to a much greater degree when genetic risk is low. (A) The marginal effects of the GxE interaction model at three values of family income: mean income and income one standard deviation above and below the mean. (B) The relationship between the residualized symptom scores (accounting for all covariates) and the SCZ‐PRS, stratified on family income (above and below the mean). ABCD, Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study; ADHD, attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder; GxE, genotype‐by‐environment interaction; SCZ‐PRS, schizophrenia‐polygenic risk score.
