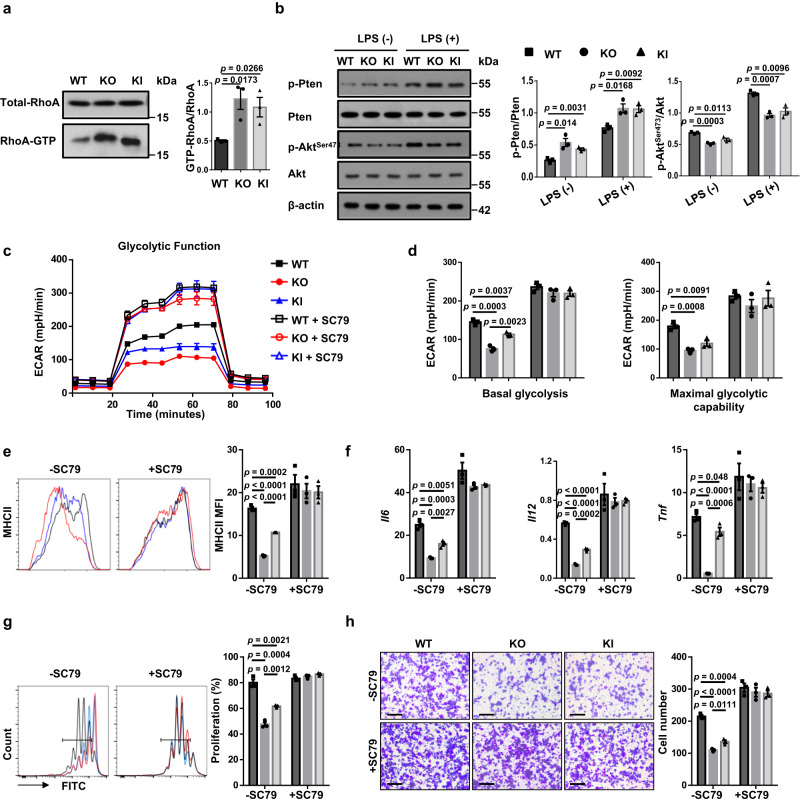
Fig. 8. ALR Myo9b KI and loss of Myo9b upregulate RhoA/Pten signaling and repress Akt-dependent glycolytic process.
a GST-pull-down and western blot analysis of RhoA activity in WT, KO, and KI BMDCs. b Results for (p-)PTEN and (p-)AKT expression in DCs with or without LPS stimulation for 1 h. c ECAR of WT, KO, and KI DCs pretreated with or without SC79 for 1 h and then stimulated with LPS for 24 h. d Baseline glycolysis and maximal glycolytic capacity in BMDCs as shown in c. e Expression of MHC II of WT, KO, and KI DCs pretreated with or without SC79 for 1 h and then stimulated with LPS for 24 h. f RT-PCR analysis of relative mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokine-encoding genes in DCs pretreated with or without SC79 for 1 h and then stimulated with LPS for 8 h. g Proliferation of CFSE-labeled BDC2.5 naive CD4+ T cells incubated with SC79- or vehicle-pretreated and BDC2.5 mimotope-pulsed WT, KO, and KI BMDCs. h Migration of DCs pretreated with or without SC79 for 1 h and then stimulated with LPS for 18 h, analyzed by transwell assay. Scale bars: 100 μm. Original magnification: ×200. n = 3 independent experiments (a-h). Values are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA.