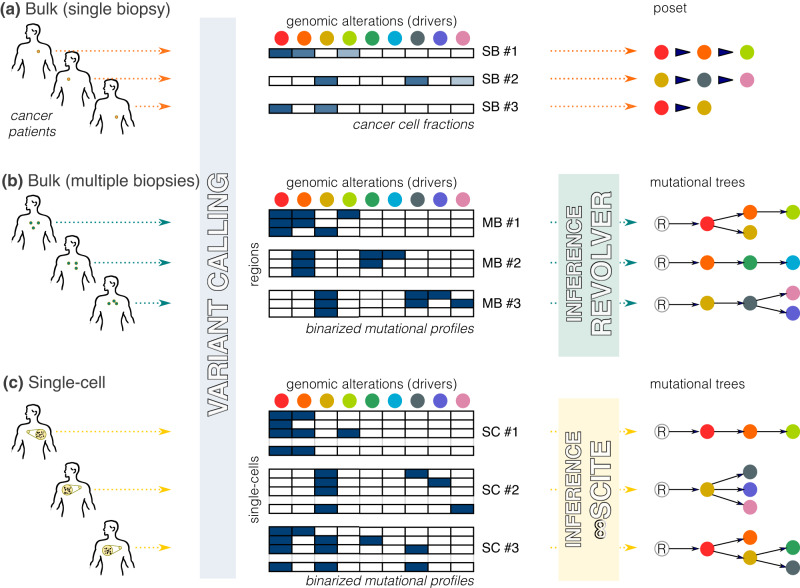
Fig. 1. ASCETIC pre-processing phase.
ASCETIC can efficiently process data at various resolutions, including the classical bulk NGS samples (a) providing a single biopsy per patient, multi-region sequencing data (b), as well as single-cell sequencing data (c). The framework includes an initial variant calling step, which can be performed adopting best practices for the considered sequencing technology. After this step, a set of mutational profiles are generated, comprising one sample per patient in the case of classical bulk NGS data, or multiple samples in the case of multiregion or single-cell data. From these inputs, ASCETIC first generates a set of temporal models of the evolution of each patient considered individually. For classical bulk NGS data, this is performed from cancer cell fractions, in order to obtain a partially ordered set (poset) for the set of driver mutations observed in each patient. For multi-region and single-cell data, ASCETIC exploits phylogenetic approaches tailored to analyze cancer data6,65,66,71,72 in order to generate a mutational tree per patient. In this work, we used REVOLVER6 for multi-region data and ∞SCITE66 for single-cell data, although any preferred state-of-the-art algorithms can be used. The generated mutational profiles and evolutionary models are given as inputs for ASCETIC next steps.