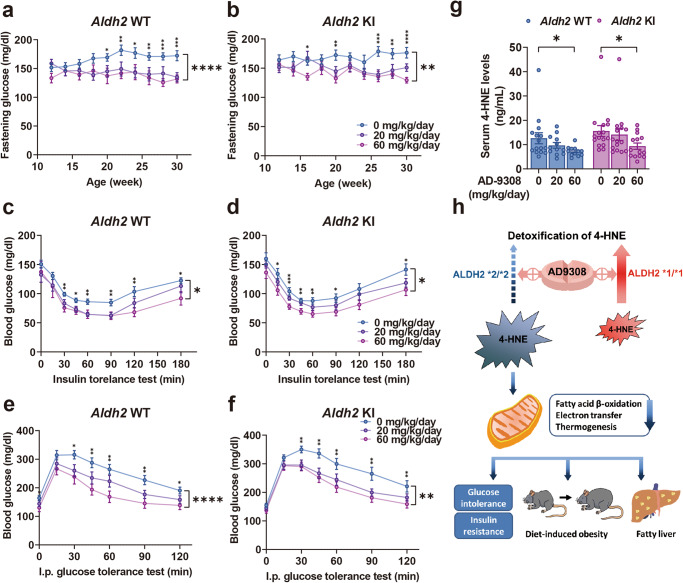
Fig. 6. ALDH2 activator AD-9308 treatment ameliorated diet-induced insulin resistance and glucose intolerance.
Fasting glucose level of the a Aldh2 wild-type(WT) and b knock-in (KI) mice treated with vehicle, low-dose AD-9308 (20 mg/kg/day), and high-dose AD-9308 (60 mg/kg/day) (repeated measures analysis of variance [ANOVA] P < 0.0001 and 0.0016). c, d Glycemic levels during the insulin sensitivity test (repeated measures ANOVA P = 0.014 and 0.012) and e, f intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test of the Aldh2 WT and KI mice treated with AD-9308 (n = 15:15 for the vehicle group; n = 14:16 for 20 mg/kg/day group; n = 9:14 for 60 mg/kg/day group; repeated measures ANOVA P < 0.0001 and 0.0039). g Serum 4-HNE (4-hydroxynonenal) levels of the Aldh2 WT and KI mice treated with AD-9308 (n = 15:16 for the vehicle group; n = 12:14 for 20 mg/kg/day group; n = 12:14 for 60 mg/kg/day group in duplicates; P-for-trend = 0.025 and 0.044) on high-fat high-sucrose diet. h Summary diagram depicting how reducing 4-HNE by AD-9308 ameliorates metabolic disturbances. Figures (a–g) were analyzed using tests for linear trends. Figures (a–e) were further analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA. All data are presented as mean and standard error (S.E.M.). The n values represent biological repeats and the number of technical repeats were expressed as duplicates or triplicates. The asterisks indicate two-sided *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.001.