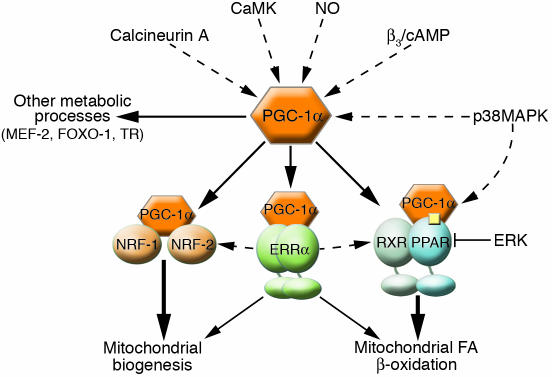
Figure 2.
PGC-1α is an integrator of the transcriptional network regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Numerous signaling pathways, including Ca2+-dependent, NO, MAPK, and β-adrenergic pathways (β3/cAMP), activate the PGC-1α directly by increasing either PGC-1α expression or activity. Additionally, the p38MAPK pathway selectively activates PPARα, which may bring about synergistic activation in the presence of PGC-1α, whereas ERK-MAPK has the opposite effect. These signaling pathways transduce physiological stimuli, such as stress, fasting, and exercise, to the PGC-1α pathway. PGC-1α, in turn, coactivates transcriptional partners, including NRF-1 and -2, ERRα, and PPARα, which regulate mitochondrial biogenesis and FA-oxidation pathways. Dashed lines indicate activation mediated by signal transduction pathways in contrast to the coactivation by PGC-1α, which is denoted by solid lines. The arrows from ERRα to the NRFs and the PPAR complex indicate that ERRα activates these pathways at the level of expression.