Figure 2.
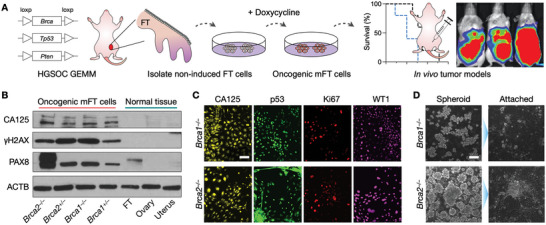
Generation and characterization of mFT cell lines. (A) FT cells were isolated from genetically engineered mice harboring mutations in Brca1 or Brca2, as well as Tp53 and Pten. Isolated cells were rendered oncogenic through the doxycycline treatment. Tumor animal models were generated by implanting the transformed cells into mice. GEMM, genetically engineered mouse model. B) Oncogenic mFT cells expressed FT‐specific protein (PAX8) and HGSOC markers (CA125, γH2AX). Normal tissue samples (uterus, ovary, FT) lacked HGSOC markers, while PAX8 was positive only with FT tissue. C) Immunofluorescence microscopy confirmed that the oncogenic mFT cells (mFT3635 and mFT3666) expressed key HGSOC markers (CA125, p53, Ki67, WT1) at the cellular level. Scale bar, 50 µm. D) Under in vitro ultra‐low adherence culture conditions, oncogenic mFT cells (mFT3635 and mFT3666) formed tumor spheroids (left). When transferred to adhesion plates, tumor spheroids adhered to the surface and spread, demonstrating their capacity to engraft. Scale bar, 100 µm.
