Figure 4.
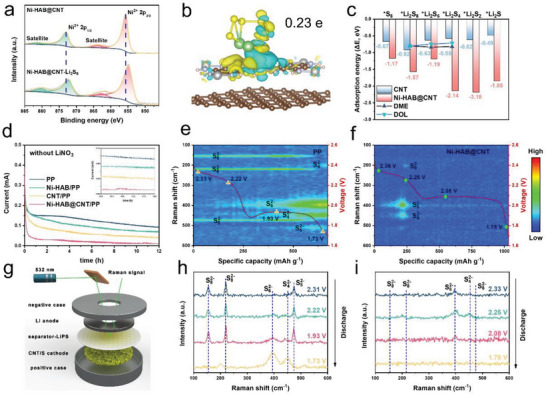
a) Ni 2p XPS spectra of Ni‐HAB@CNT before and after adsorption of Li2S6; b) density functional theory (DFT) simulations: the optimized adsorption configurations of Li2S6 interacted with Ni‐HAB@CNT and corresponding different charge density (DCD) analysis, the value of the isosurface is set to be 0.001 e Å−3; c) comparison of adsorption energies of Li2S n with Ni‐HAB@CNT, CNT, and electrolyte solvent molecules (DME and DOL); d) the shuttle currents of Li‐S batteries with PP, Ni‐HAB/PP, CNT/PP, and Ni‐HAB@CNT/PP as the separators; e,f) in situ time‐resolved Raman spectra obtained during the discharging processes with PP and Ni‐HAB@CNT modified separators. g) Schematic illustration of a Li‐S battery toward in situ Raman tests; h,i) selected Raman spectra of Li‐S cells based on PP and Ni‐HAB@CNT modified separators. The red curves represent the discharging processes.
