Figure 4.
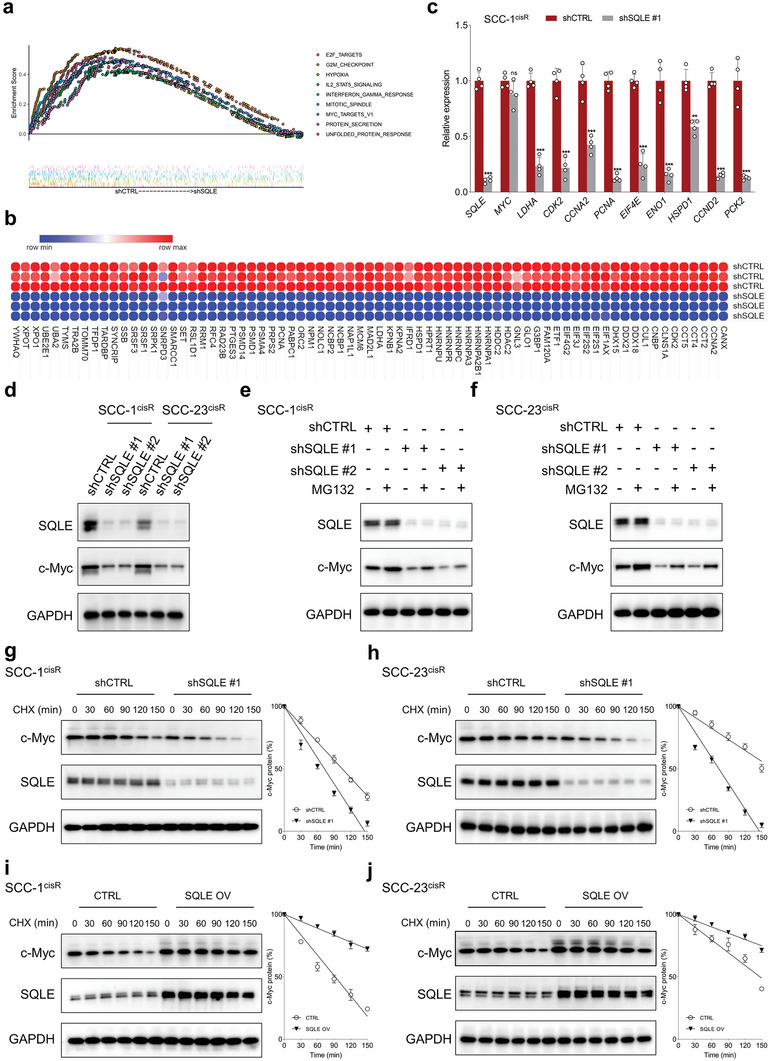
SQLE inhibition destabilizes c‐Myc and impairs its transcriptional activity. a) GSEA analysis shows significant enrichment of genes in the MYC_TARGETS_V1 molecular signature in SCC‐23cisR cells without SQLE depletion. b) Heatmap depicting aberrant expression of c‐Myc target genes upon SQLE depletion in SCC‐23cisR cells. c) qRT‐PCR analysis of representative c‐Myc‐induced target genes in SCC‐1cisR cells following SQLE depletion (n = 4). d) Expression of c‐Myc and SQLE in SCC‐1cisR and SCC‐23cisR cells upon SQLE knockdown. e,f) SQLE‐depleted SCC‐1cisR and SCC‐23cisR cells treated with MG132 (20 µm, 8 h) before harvest, with SQLE and c‐Myc expression analyzed by western blotting. g,h) Time‐course analysis of c‐Myc and SQLE expression in SCC‐1cisR and SCC‐23cisR cells with or without SQLE depletion. Cells treated with CHX (100 µg mL−1) for varying periods. i,j) SCC‐1cisR or SCC‐23cisR cells with or without SQLE overexpression were treated with 100 µg mL−1 CHX for indicated time periods; western blotting performed to analyze dynamic changes in c‐Myc and SQLE. Data were presented as mean ± SD. ns (not significant), **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for Student's t‐test.
