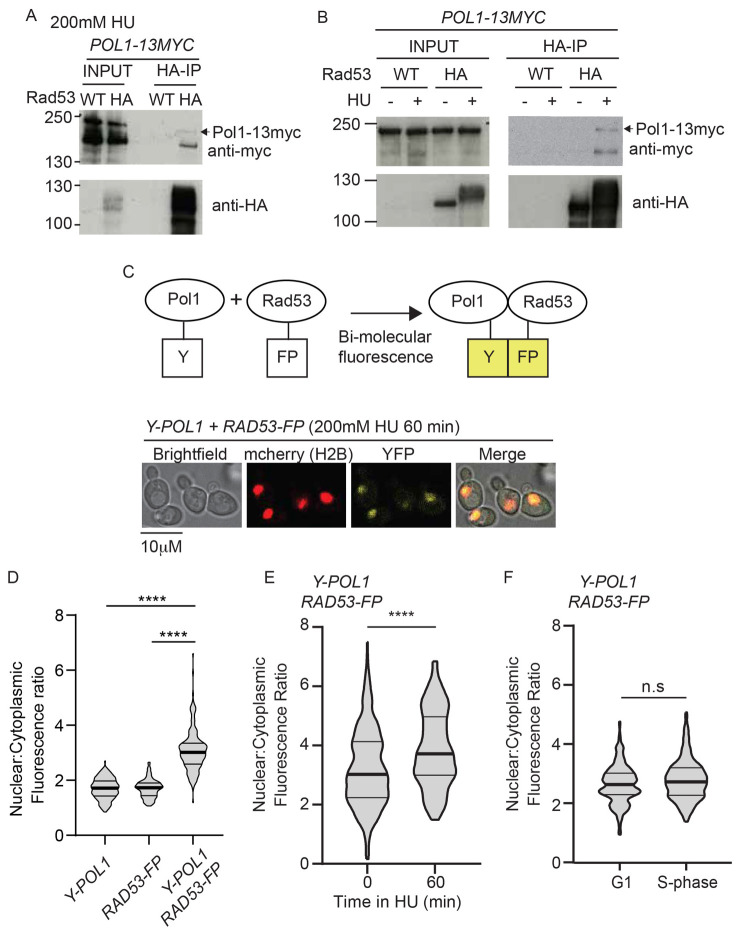
Figure 3. Rad53 interacts with Polymerase alpha in vivo.
A) Anti-HA immunoprecipitation (IP) from a RAD53 wild type (WT) strain or a strain containing internally tagged Rad53-6HA (HA). All strains contain POL1-13myc and were arrested in 200 mM HU. B) As a), except IP performed from strains released from G1 phase into S-phase in the presence (+) or absence (-) of HU. C) Top, schematic diagram of bi-molecular fluorescence assay. Endogenous Pol1 was N-terminally tagged with a fragment of YFP (Y), while Rad53 was internally tagged with the remaining fragment of YFP (FP). Interaction between Pol1 and Rad53 would bring together the two halves of YFP to allow fluorescence (in yellow). Bottom, example images of yeast containing these YFP fragment tagged Pol1/Rad53 constructs treated with 200 mM HU for 60 minutes after release from G1 phase. Strains also contain H2B-mcherry to delineate the nucleus. D) Violin plot of the nuclear to cytoplasmic fluorescence ratio of strains containing the individual YFP fragment alleles or both. These cells were released from G1 phase into 200 mM HU for 60 minutes. n>150, p-value from a t-test **** < 0.0001. E) Violin plot of the YFP fluorescence ratio, as in d) from cells containing both Y-Pol1 and Rad53-FP, released from G1 phase (0) into 200 mM HU for 60 minutes. n>100, p<0.0001 (****). F) As e), except cells were released into S-phase in the absence of HU for 60 minutes. n>150, n.s = not significant.