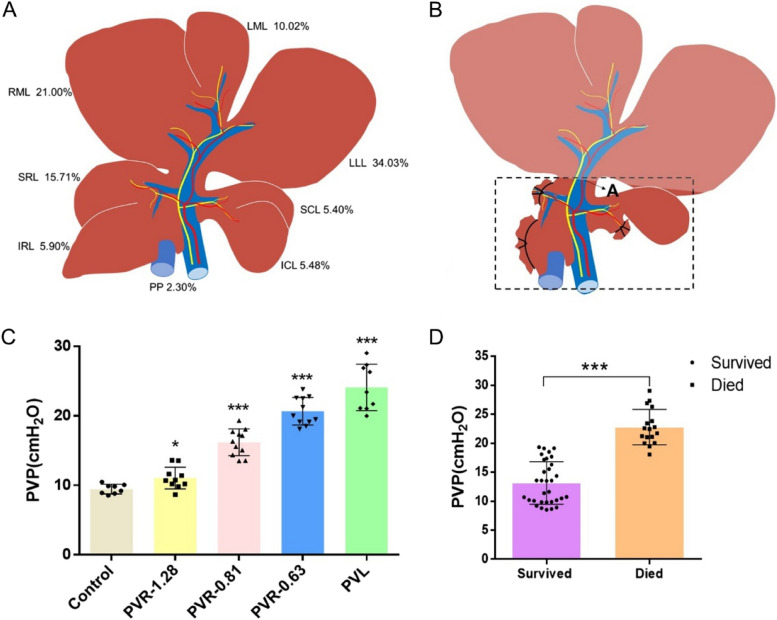
Fig. 1.
An extreme ALPPS model in rats was established, and the PVL procedure spurred the significant increase in PVP. A Schematic representation of SD rat liver. B Schematic representation of the extreme ALPPS model. SCL and part of PC were designed as the ideal future liver remnant (FLR, indicated in the dashed frame), as it represents approximately 6.5% of the total liver parenchyma. During the step I procedure, the SRL, IRL and ICL were removed, the PV was ligated or restricted at point A. The RML, LML and LLL were planned to be resected during the step III surgery. C The PV (at point A) was subjected to ligation or restriction at different degrees, and the portal vein pressure (PVP) was measured. (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). D PVPs of rats between the died and survived groups were retrospectively compared. (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). ALPPS, Associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy; FLR, future liver remnant; ICL, inferior caudate lobe; IRL, inferior right lobe; LLL, left lateral lobe; SCL, superior caudate lobe; SRL, superior right lobe; RML right medial lobe; LML left median lobe; PC pericaval tissue; PV, portal vein PVP; portal vein pressure