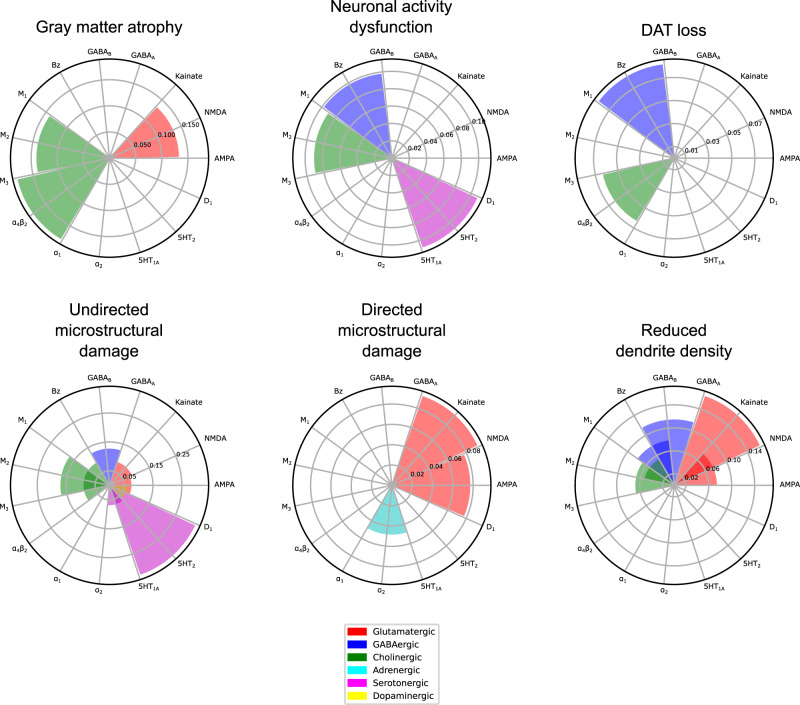
Fig. 4. Receptors mediating degenerative alterations to different macroscopic biological factors in PD.
The combined statistically stable model effects of each receptor type on each biological factor are shown. The muscarinic M2 and nicotinic α4β2 receptors contribute significantly to gray matter density, neuronal activity and dopamine transporter alterations. The Bz site is prominently associated with activity and dopamine transporter alterations. The serotonergic 5HT2 receptor is involved in functional and microstructural (MD) alterations, while glutamatergic effects are marked by NMDA affecting gray matter atrophy, AMPA and kainate affecting directed microstructural damage (FA) and kainate affecting dendrite density (t1/t2), respectively. Notably, the D1 receptor distribution is relatively homogeneous and not marginally informative in the presence of DAT imaging.