Fig. 2.
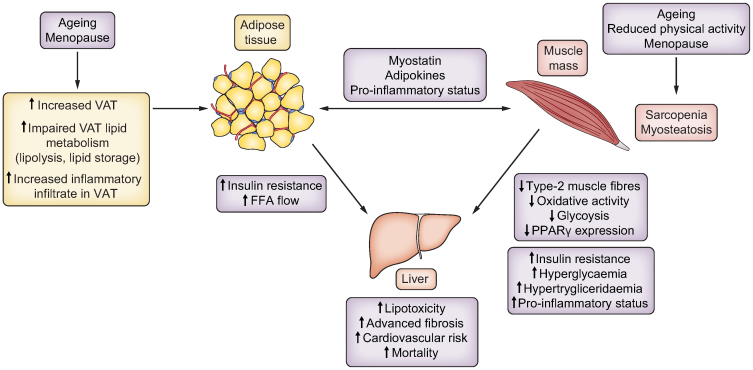
Interactions between adipose tissue, muscle and liver contribute to the development and progression of NAFLD in women.
Adipokines and myokines (such as myostatin) mediate adipose tissue-muscle interactions. Ageing and the menopause (i.e. oestrogen deficiency) increase VAT depots and reduce muscle mass and quality. Expanded VAT depots increase FFA delivery to the liver, which has detrimental effects. These alterations in body composition contribute to insulin resistance, hyperglycaemia and/or hyperlipidaemia, with consequent development and progression of NAFLD. FFA, free fatty acid; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; VAT, visceral adipose tissue.