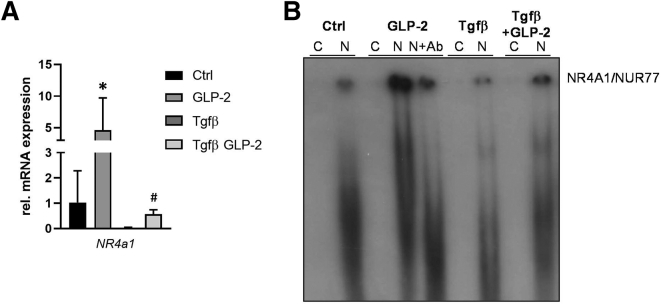
Figure 4.
GLP-2 treatment increases NR4a1/Nur77 expression and nuclear binding in human hepatic stellate cells in vitro. (A) Real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to assess the mRNA expression of NR4a1/Nur77 in the human hepatic stellate cell line LX-2. Tgfβ-induced suppression of NR4a1/Nur77 could be counteracted by GLP-2 treatment. mRNA expression values were normalized against 36b4 levels and are shown relative to expression level in untreated control cells. ∗Significant difference from untreated control (Ctrl) cells. #Significant difference from Tgfβ-treated cells. P < .05. (B) Representative electrophoretic mobility shift assay demonstrated that GLP-2 treatment increases the nuclear binding of NR4A1/NUR77, whereas Tgfβ challenge led to a reduction of the NR4A1/NUR77 nuclear binding. Of note, GLP-2 treatment was able to counteract the Tgfβ-related reduction of the NR4A1/NUR77 nuclear binding. Ab, antibody; C, cytoplasmatic protein fraction; N, nuclear protein fraction.