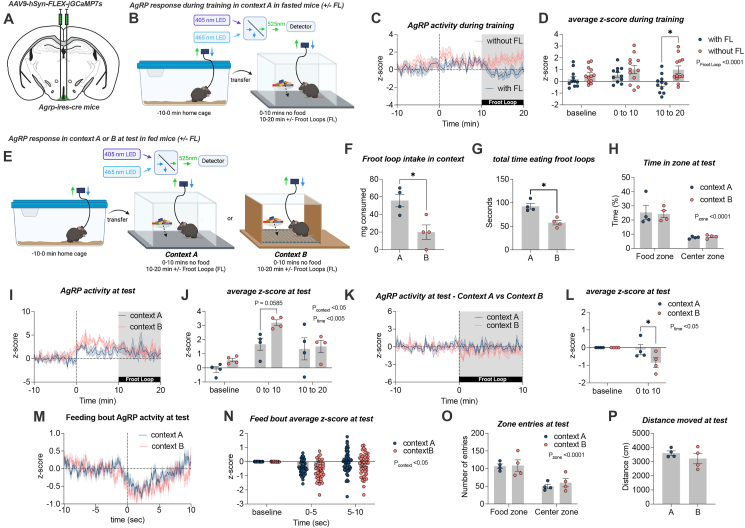
Figure 2.
Context-specific AgRP neuronal population activity during CIF. (A) Agrp-ires-cre mice received bilateral injections of AAV9-syn-FLEX-jGCaMP7f into the arcuate nucleus for photometry experiments. (B) Experimental overview of GCaMP7f recordings during context A training created with BioRender.com. All mice were trained under fasted conditions and received Froot Loops (FL) after 10 min. (C) The presentation of Froot Loops (FL) within context A after 10 min reduced AgRP neuronal activity (data normalised to −10 to 0 baseline period; with FL n = 11; without FL n = 12). (D) Average AgRP z-score response during training in context A at baseline (−10 to 0), 0–10 and 10–20 min after Froot Loop presentation (FL). (E) Experimental overview of AgRP GCaMP7f recordings during CIF test in ad libitum fed mice; created with BioRender.com. (F) Mice that underwent the CIF protocol coupled with photometry showed increased Froot Loops consumption and (G) total time eating in context A compared to context B at test (paired t-test, n = 4). (H) At CIF test, mice spent more time in the food zone compared to the centre zone (two-way RM ANOVA; main effect of zone), however no differences were observed between context A and B. (I) AgRP neuronal activity in context A and B for the entire test period; Froot Loops were presented after 10 min (data normalised to −10 to 0 baseline period; n = 4). (J) Average AgRP z-score response at baseline (−10 to 0), 0–10 and 10–20 min in context A and B at test (two-way RM ANOVA main effect of context and time, Sidak's multiple comparisons post hoc analysis; n = 4). (K) AgRP neuronal response to the presentation of Froot Loops into the test context. Time 0 represents the addition of Froot Loops into the test context (data normalised to −10 to 0 baseline period; n = 4). (L) Average AgRP z-score response prior to introducing Froot Loops (−10 to 0) and 0 to 10 in context A and B at test (two-way RM ANOVA main effect of time, Sidak's multiple comparisons post hoc analysis; n = 4). (M) AgRP neuronal activity during each feeding bout within context A and B at test. Time 0 represents contact with food (data normalised to −10 to 0 s baseline period; n = 4). (N) The average AgRP z-score response to each feeding bout within context A and B at baseline (−10 to 0 s), 0–5 and 5–10 s; (two-way RM ANOVA main effect of context; n = 56 and 48 events from 4 mice in context A and B respectively). (O) At CIF test, mice made more entries in the food zone compared to the centre zone (two-way RM ANOVA; main effect of zone), however no differences were observed between context A and B (n = 4). (P) There was no difference in distance moved at test in context A and B. Dotted line in C &I represents time mice were transferred in the context. Dotted line in K represents the time Froot Loops were added during the CIF test. Dotted line M presented the time of food contact for each feeding bout. Values are presented as mean ± SEM, ∗p < 0.05. All specific statistical information is reported in Supplemental Table 1.