Fig. 3. The circadian clock protects from systemic acute IR-induced toxicity.
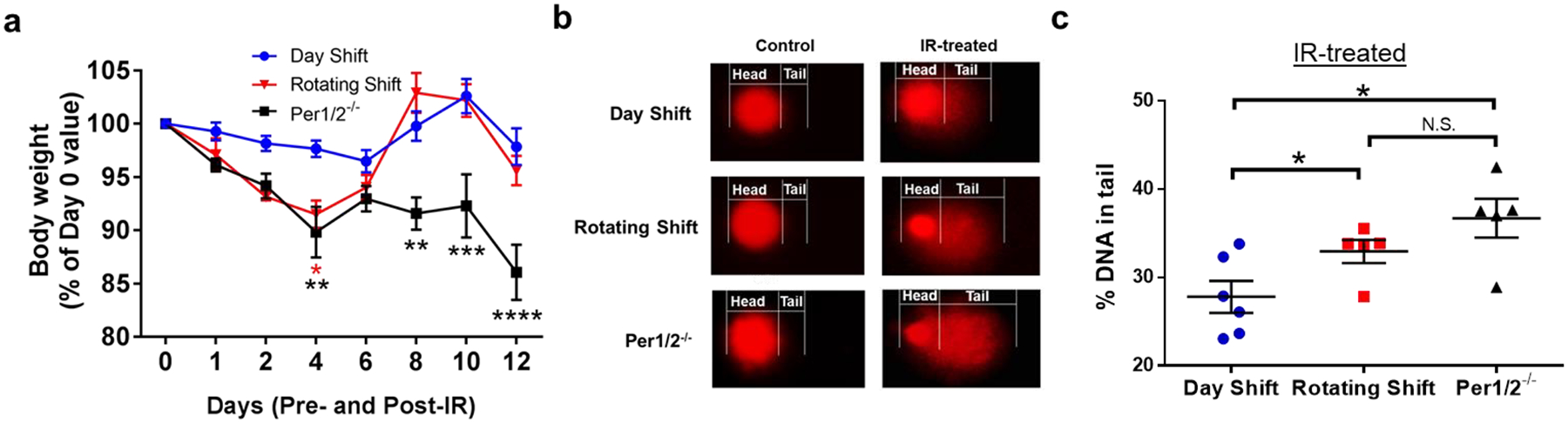
. a) Body weights were measured pre- (day 0) and post-IR (days 1–12). b) Representative images of alkaline comet assay to detect DNA strand breaks from SKH-1 mouse blood cells in control and IR-treated mice collected on day 13. c) Quantification of genomic DNA as % DNA in tail. Repeated Measures Two-way ANOVA and two-tailed student’s t-tests were used to compare body weights and comet assay analysis respectively to control/D.S. group *=p<0.05. **=p<0.01, ***=p<0.001, ****=p<0.0001. Error bars = S.E.M. N.S. means not significant. (n=5–6 mice per group).
