Fig. 2.
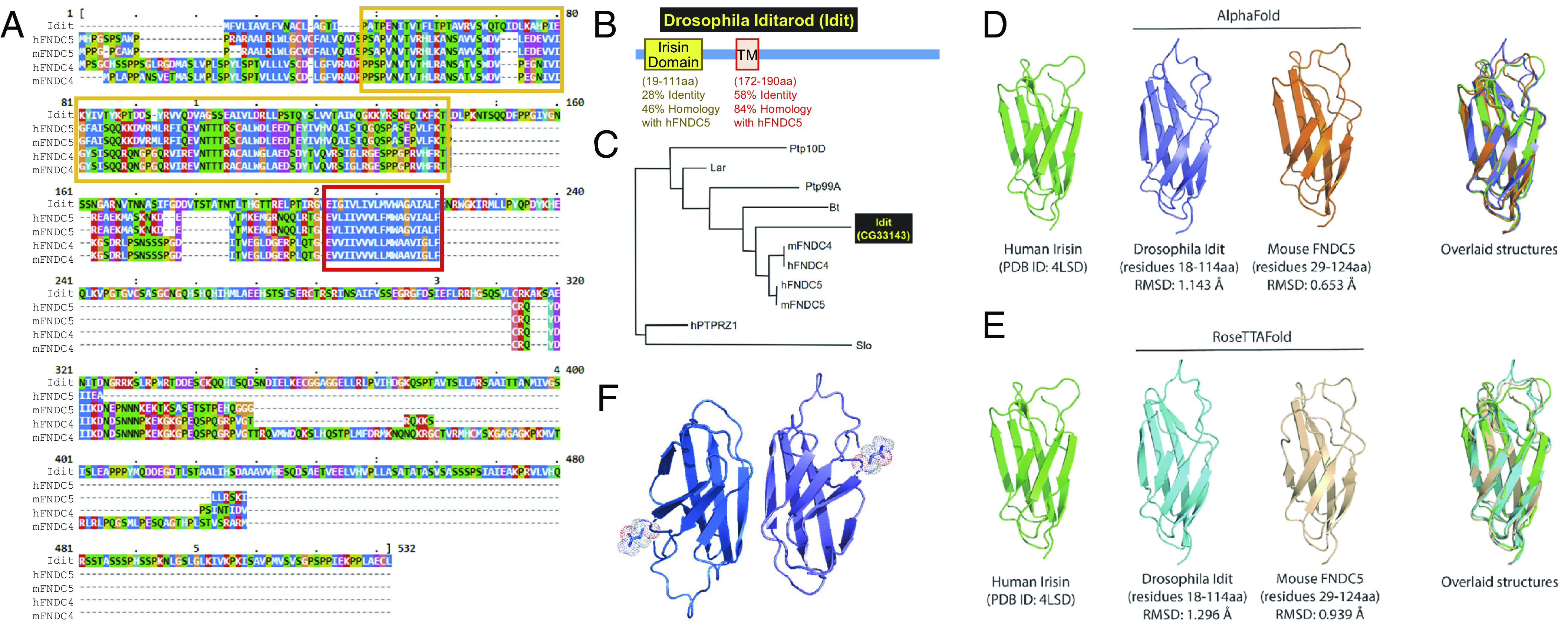
Idit encodes Drosophila homolog of Irisin/FNDC5. (A) Multiple sequence alignment using Drosophila Idit, human and mouse FNDC5, and human and mouse FNDC4, conducted with ClustalW. Hydrophobic residues are shaded in blue, polar residues in green, acidic residues in purple, basic residues in red, cysteine in orange, glycine in tan, proline in light green. Irisin domain is indicated by yellow box. Transmembrane domain (TM) is indicated by red box. (B) Idit has two domains that show substantial homology to human FNDC5—extracellular Irisin domain and TM domains. Homology of each domain to human FNDC5 is assessed after Needleman–Wunsch alignment of each domain. For additional protein domains, see SI Appendix, Fig. S3C. (C) Phylogenetic tree constructed using different proteins possessing Irisn/FNDC5-like sequences, conducted with PhyML. Drosophila, human and mouse species are identified as prefixes d, h, and m, respectively. (D and E) AlphaFold (D) and RoseTTAFold (E) predictions of Irisin homology domains from mouse FNDC5 and Drosophila Iditarod, compared with each other and human Irisin crystal structure (PDB: 4LSD). Cα RMSD is used for measuring the structural similarity in between. (F) The potential dimer model of AlphaFold-predicted Iditarod overlaid on the human Irisin dimer. The predicted glycosylation site of Asn residues (NxT motif) are displayed as stick/dot model.
