Fig. 5.
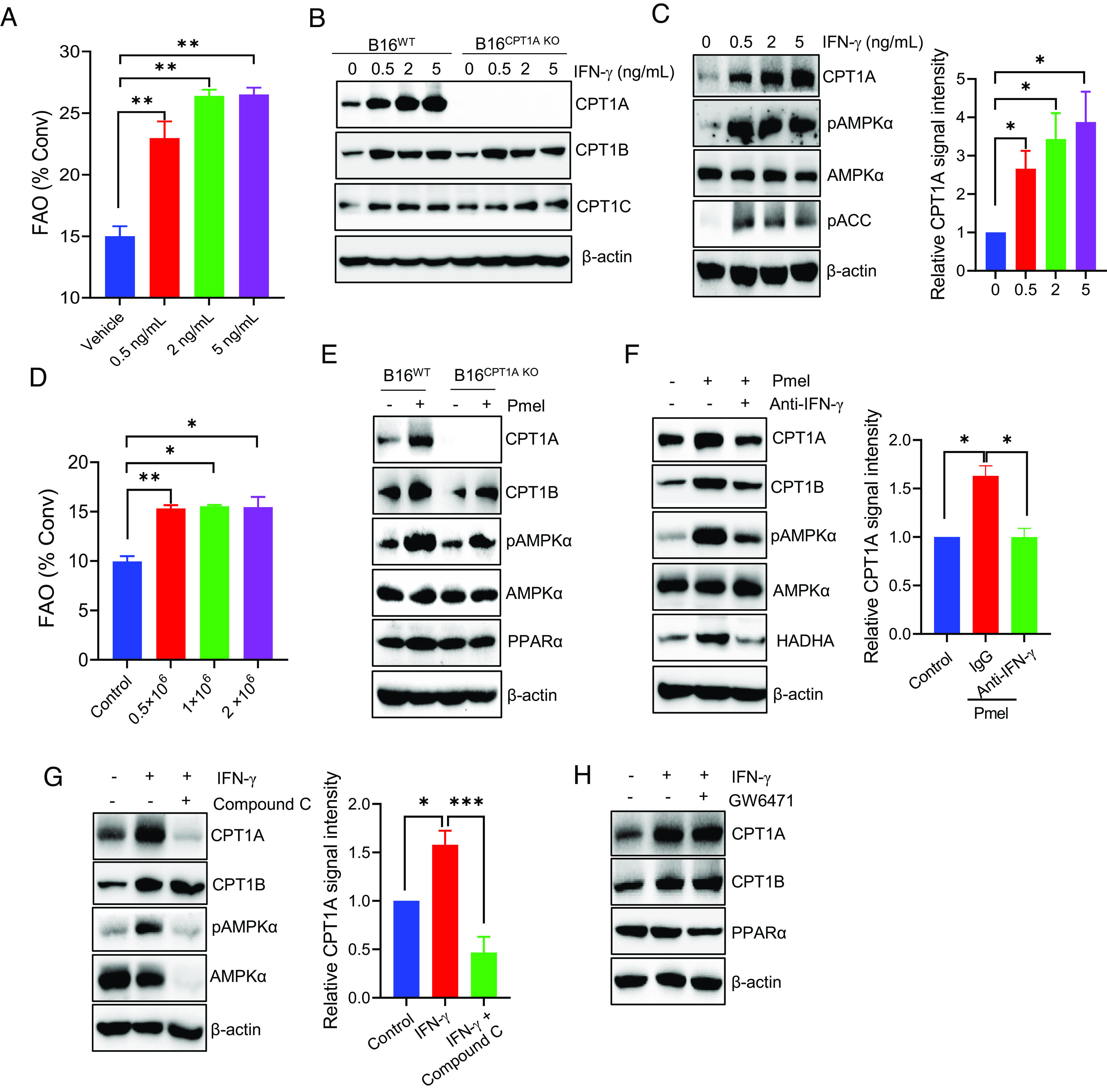
T cell–derived IFN-γ up-regulates CPT1A-mediated FAO in an AMPK-dependent manner. (A) B16 tumor cells were stimulated with IFN-γ at indicated concentrations for 24 h. The FAO activity was determined by measuring conversion of 3H-palmitic acid to 3H2O. (B) The expression of CPT1 enzymes in IFN-γ-treated B16WT or B16CPT1A KO cells was examined by immunoblotting. (C) Analysis of CPT1A, AMPKα, or phosphorylation of AMPKα and ACC in B16 cells after treatment with IFN-γ. (D) B16 cells and Pmel cells were plated into the lower and upper chambers of the transwells, respectively. The FAO activity in B16 cells was determined by diffusion assays after coculture. (E) Immunoblotting analysis of the levels of CPT1A, phosphorylated AMPKα, AMPKα, and PPARα in B16WT or B16CPT1A KO cells after coculture with T cells in transwells plates. (F) B16 cells were cocultured with activated T cells in transwell assays in the presence or absence of IFN-γ-neutralizing antibodies, followed by immunoblotting analysis of CPT1A, pAMPKα, or HADHA in tumor cells. (G and H) B16 tumor cells were treated with IFN-γ (5 ng/mL) in the presence of the AMPKα inhibitor Compound C (G) or PPAR inhibitor GW6471 (H) for 24 h. Immunoblotting was performed to determine the levels of CPT1 enzymes or pAMPKα. Data are representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001.
