Fig. 6.
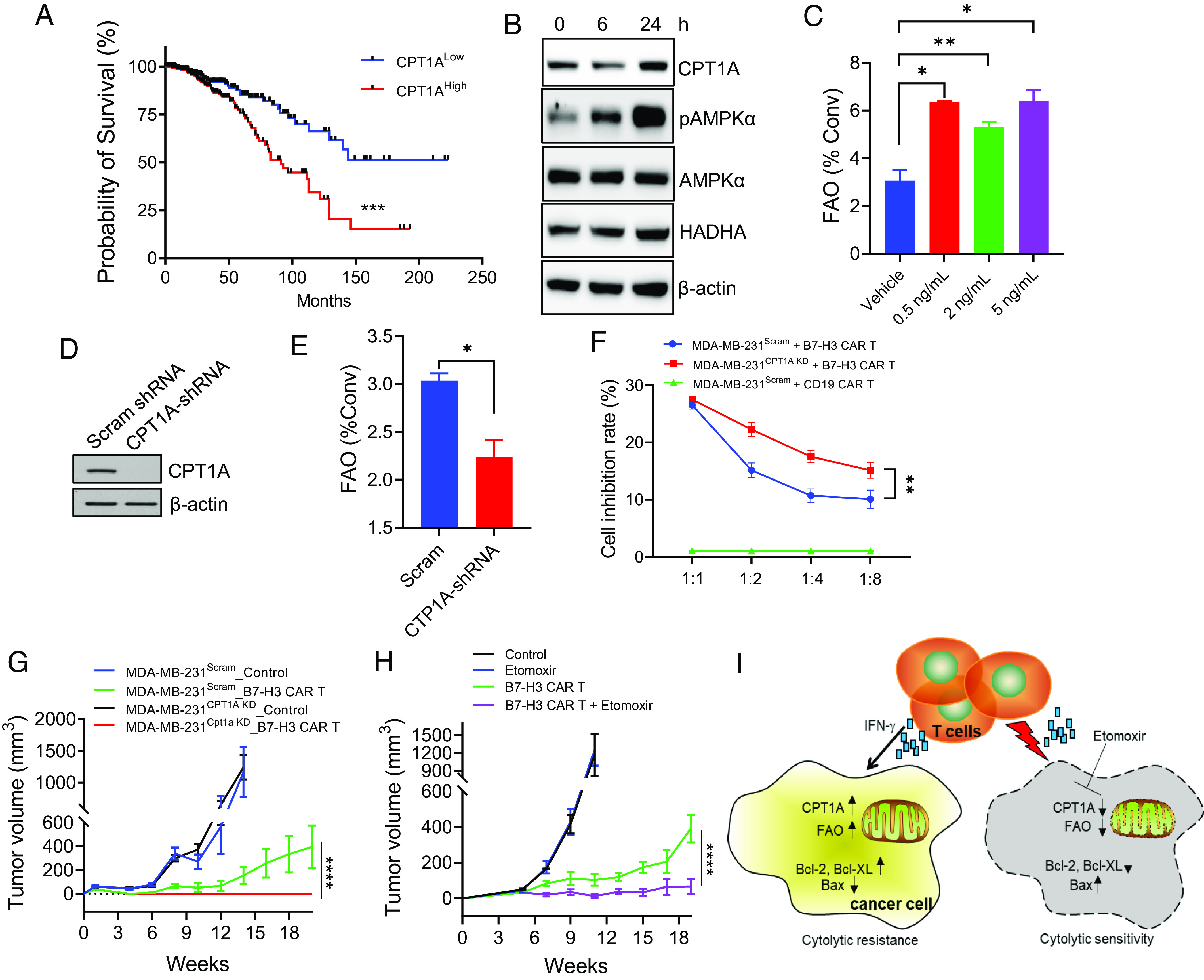
Blockade of FAO improves human breast cancer responsiveness to CAR T therapy. (A) The publicly available data on Oncomine were used to analyze the correlation of CPT1A mRNA expression and survival in patients with breast cancer. Kaplan–Meier survival and Gehan–Breslow–Wilcoxon test of two groups were performed using GraphPad PRISM software. (B) Human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells were stimulated with IFN-γ and analyzed for expression of CPT1 enzymes, pAMPKα, PPARα, or HADHA. (C) FAO analysis of MDA-MB-231 cells after IFN-γ stimulation at different concentrations. (D) Knockdown (KD) of CPT1A in MDA-MB-231 cells by short hairpin RNA (shRNA) was confirmed in comparison with those transduced with scramble shRNA. (E) FAO activity in MDA-MB-231Scram or MDA-MB-231CPT1A KD cells was measured by quantifying the conversion of 3H-palmitic acid to 3H2O. (F) MDA-MB-231 cells with or without CPT1A KD were cocultured with B7-H3 CAR T cells for 48 h followed by MTT assays. (G) NSG mice (n = 5) with MDA-MB-231 tumors with or without CPT1A KD were treated with B7-H3 CAR T cells (2 × 106 cells, i.v.) 1 wk after tumor implantation. (H) NSG mice with MDA-MB-231 tumors were treated with B7-H3 CAR T cells 5 wk after tumor implantations. Etomoxir treatment was initiated 1 d before CAR T therapy and administered daily during the course of study. Data are representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001. ****P < 0.0001. (I) Schematic illustration of tumor resistance to immune cytolysis by IFN-γ-induced FAO in cancer cells. Upon recognition and destruction of tumor targets, IFN-γ-derived from activated T cells results in FAO elevation in cancer cells by inducing CPT1A expression via AMPKα activation. Activation of this metabolic pathway confers cancer cell resistance to immune effector cells by promoting prosurvival signaling, e.g., upregulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL and downregulation of Bax. Targeted inhibition of CPT1A or blockade of FAO (e.g., Etomoxir) can enhance proapoptotic signaling, thereby potentiating tumor sensitivity to immune killing.
