Abstract
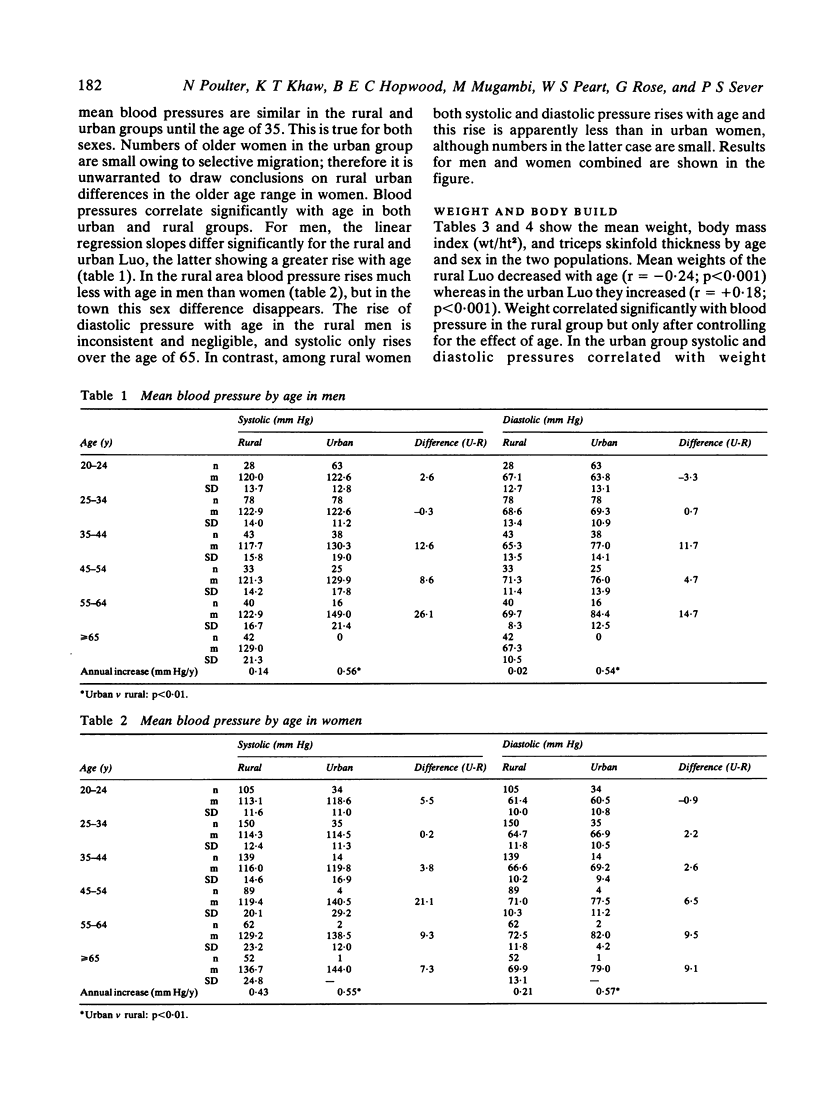
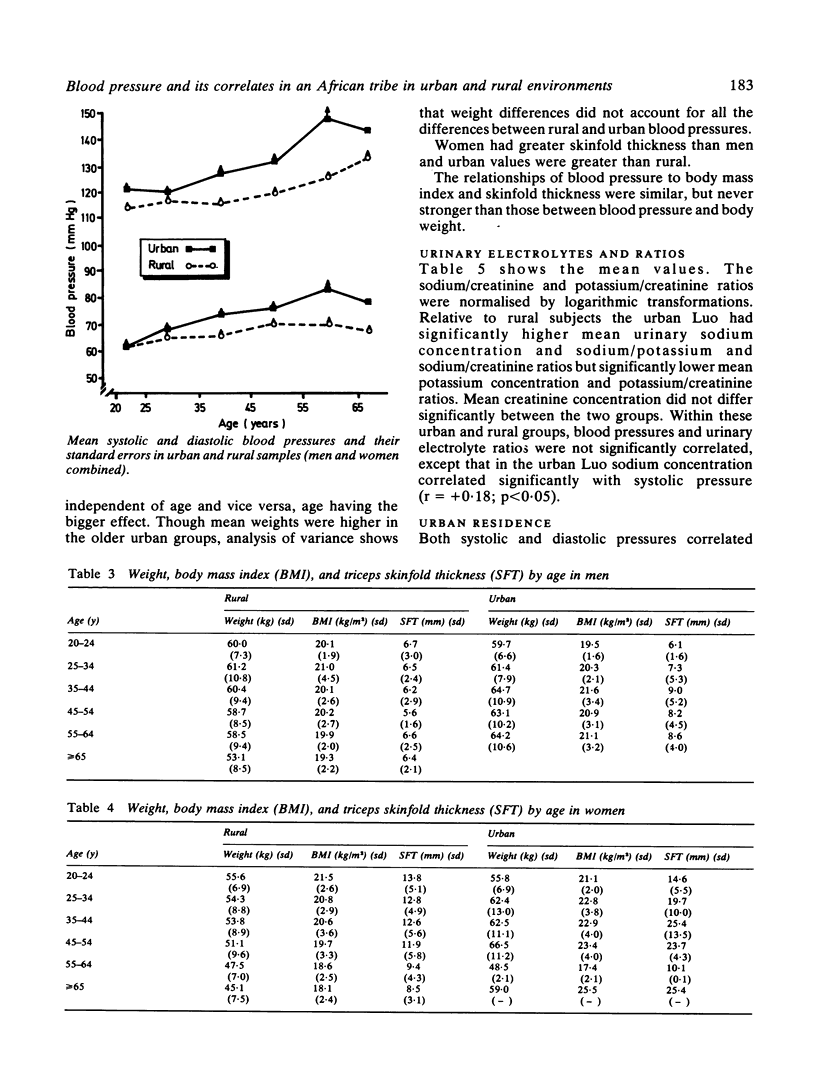
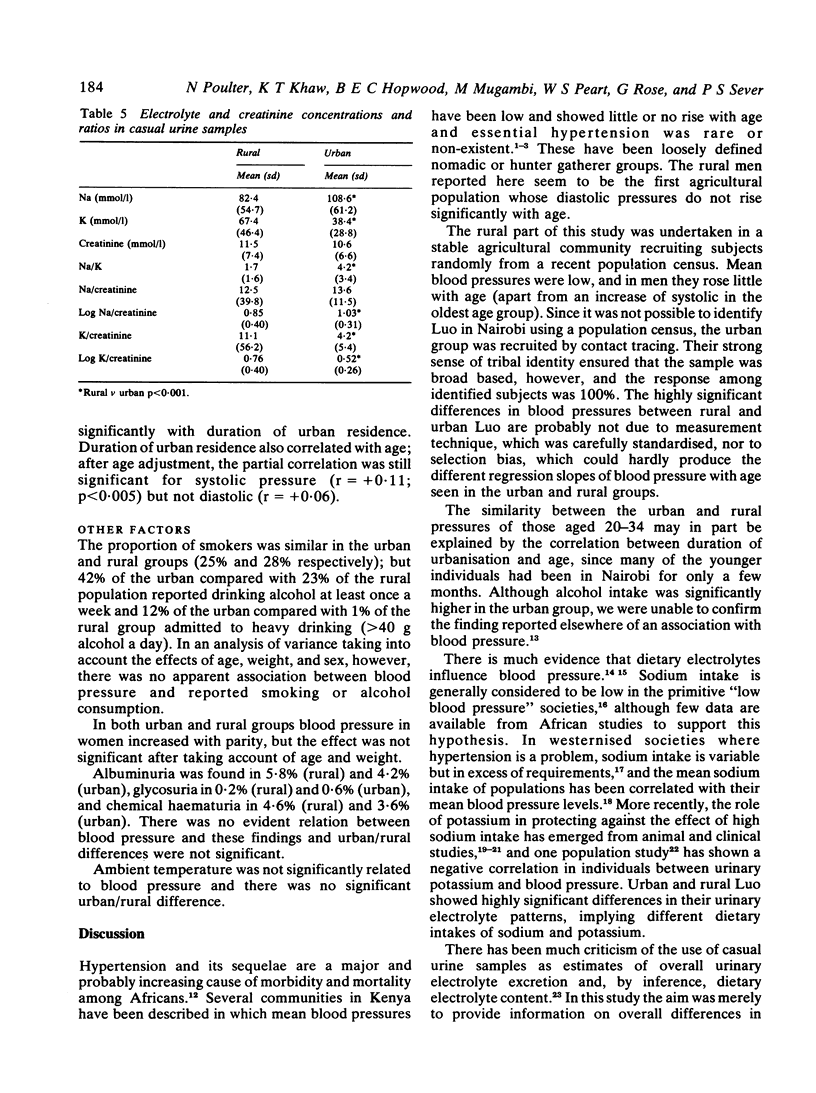
As part of a longitudinal study of migrants who move from a subsistence farming rural society to Nairobi, blood pressures and associated factors were measured in cross sectional studies of members of the Luo tribe in their traditional rural environment and in the urban environment of Nairobi. Blood pressures in Nairobi correlated with duration of urban residence. In the rural area men showed a negligible rise in blood pressure with age, and both sexes showed a significantly smaller rise than in the urban area. Although mean weights of the rural group were smaller, this did not account for all the urban/rural differences in blood pressures. Nevertheless, mean urinary sodium concentration and sodium ratios (sodium/potassium and sodium/creatinine) were significantly higher in the urban group whereas mean urinary potassium concentration and potassium/creatinine ratio were significantly lower. Perhaps the ratio of sodium to potassium in the diet contributes to the different blood pressure profiles of these two populations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAHL L. K. Salt intake and salt need. N Engl J Med. 1958 Jun 5;258(23):1152–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195806052582305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl L. K. Salt and hypertension. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Feb;25(2):231–244. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.2.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatsky A. L., Friedman G. D., Siegelaub A. B., Gérard M. J. Alcohol consumption and blood pressure Kaiser-Permanente Multiphasic Health Examination data. N Engl J Med. 1977 May 26;296(21):1194–1200. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197705262962103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever A. F., Beretta-Piccoli C., Brown J. J., Davies D. L., Fraser R., Robertson J. I. Sodium and potassium in essential hypertension. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Aug 15;283(6289):463–468. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6289.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu K., Cooper R., McKeever J., McKeever P., Byington R., Soltero I., Stamler R., Gosch F., Stevens E., Stamler J. Assessment of the association between habitual salt intake and high blood pressure: methodological problems. Am J Epidemiol. 1979 Aug;110(2):219–226. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANN G. V., ROELS O. A., PRICE D. L., MERRILL J. M. Cardiovascular disease in African Pygmies. A survey of the health status, serum lipids and diet of Pygmies in Congo. J Chronic Dis. 1962 Apr;15:341–371. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(62)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANN G. V., SHAFFER R. D., ANDERSON R. S., SANDSTEAD H. H. CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE IN THE MASAI. J Atheroscler Res. 1964 Jul-Aug;4:289–312. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(64)80041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneely G. R., Battarbee H. D. High sodium-low potassium environment and hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1976 Nov 23;38(6):768–785. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(76)90356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page L. B. Epidemiologic evidence on the etiology of human hypertension and its possible prevention. Am Heart J. 1976 Apr;91(4):527–534. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(76)80337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE G. STANDARDISATION OF OBSERVERS IN BLOOD-PRESSURE MEASUREMENT. Lancet. 1965 Mar 27;1(7387):673–674. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91827-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAPER A. G., WILLIAMS A. W., SPENCER P. Blood-pressure and body build in an African tribe living on a diet of milk and meat. East Afr Med J. 1961 Dec;38:569–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sever P. S., Gordon D., Peart W. S., Beighton P. Blood-pressure and its correlates in urban and tribal Africa. Lancet. 1980 Jul 12;2(8185):60–64. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92940-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper A. G., Leonard P. J., Jones K. W., Jones M. Environmental effects on the body build, blood pressure and blood chemistry of nomadic warriors serving in the army in Kenya. East Afr Med J. 1969 May;46(5):282–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper A. G., Wright D. H., Kyobe J. Blood pressure and body build in three nomadic tribes of northern Kenya. East Afr Med J. 1969 May;46(5):273–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truswell A. S., Kennelly B. M., Hansen J. D., Lee R. B. Blood pressures of Kung bushmen in Northern Botswana. Am Heart J. 1972 Jul;84(1):5–12. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(72)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. M., Dore C. F. A random-zero sphygmomanometer. Lancet. 1970 Feb 14;1(7642):337–338. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90709-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


