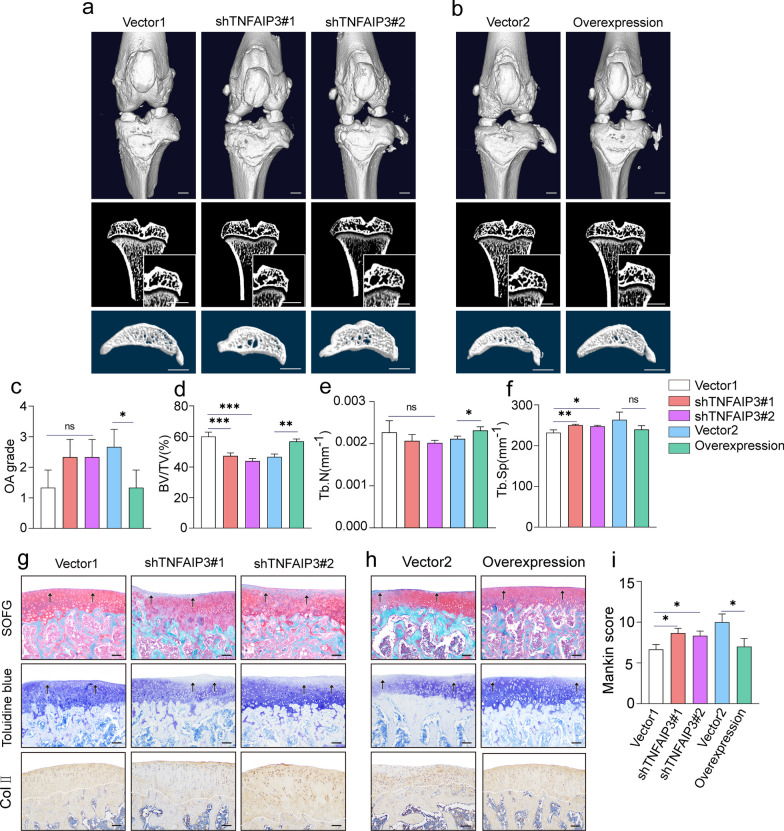
Fig. 7.
ACSC-specific TNFAIP3 overexpression ameliorates surgery-induced OA in rats. a, b 3D reconstruction of rat knee joints (top), tibial subchondral bone medial compartment (sagittal view) (bottom), and microCT images of rat tibia subchondral bone (coronal view) (middle) showed that TNFAIP3-overexpression ACSCs significantly improved the osteochondral structure, while TNFAIP3-knockdown ACSCs lead to poor protection effects in OA rats at 4 week after injection (n = 3). Scale bars, 2 mm. c OA grade was rated by quantification of the degree of cartilage loss and osteophytes from micro-CT. d–f Micro-CT measurements for bone volume fraction (BV/TV) (d), trabecular number (Tb.N) (e) and trabecular separation (Tb.Sp) (f) in the subchondral bone of vector-transfected and TNFAIP3-overexpress or knockdown ACSCs rats at 4 w after injection. g, h Representative images of safranin O–fast green staining (top), toluidine blue staining (middle), and type II collagen immunostaining (bottom) in the subchondral bone showed that TNFAIP3-overexpression ACSCs significantly improved the pathological changes in the osteochondral regions of OA rats, while TNFAIP3-knockdown ACSCs lead to poor effects in OA models at 4 w post-surgery. Scale bars, 200 μm. i Mankin scores of osteoarthritic rat knees at 4 w after injection. The statistical significance of differences was determined using one-way ANOVA with multiple comparison tests (LSD). All data are shown as the mean ± S.D. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant