FIGURE 2.
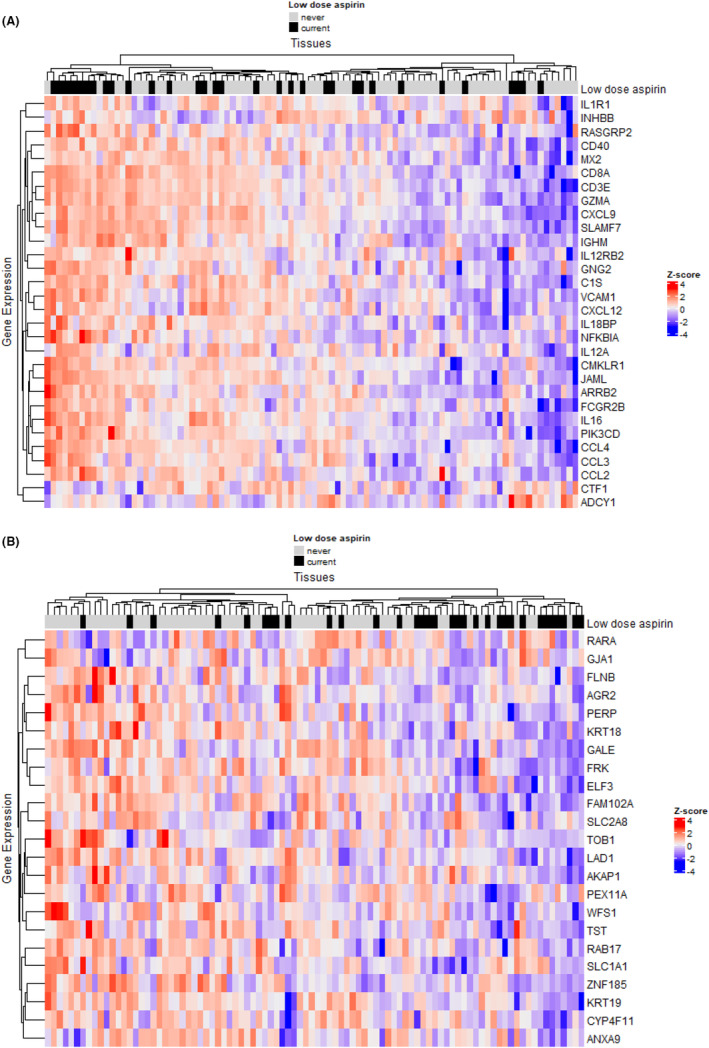
Differentially expressed genes included in significant pathways associated with current versus never low‐dose aspirin use in type II ovarian tumors. (A) Differentially expressed inflammation and immune‐related pathway genes that are associated with current versus never low‐dose aspirin use in type II ovarian tumors. Within the significant pathways (i.e., interferon‐gamma response, chemokine signaling pathway, chemokine receptors bind chemokine, cytokine‐cytokine receptor interaction, allograft rejection, immunoregulatory interactions between a lymphoid and a nonlymphoid cell, primary immunodeficiency, antigen activates B‐cell receptor BCR leading to generation of second messengers, and FCGR activation), individual genes that were associated with current low‐dose aspirin use with unadjusted p‐value <0.10 were included in the heatmap. (B) Differentially expressed estrogen‐related pathway genes that are associated with current versus never low‐dose aspirin use in type II ovarian tumors. Within the significant pathways (i.e., estrogen response late and estrogen response early), individual genes associated with current low‐dose aspirin use with unadjusted p‐value<0.10 were included in the heatmap.
