Figure 3. THBD-PAR1 axis enables senescent hepatocyte accumulation during NAFLD.
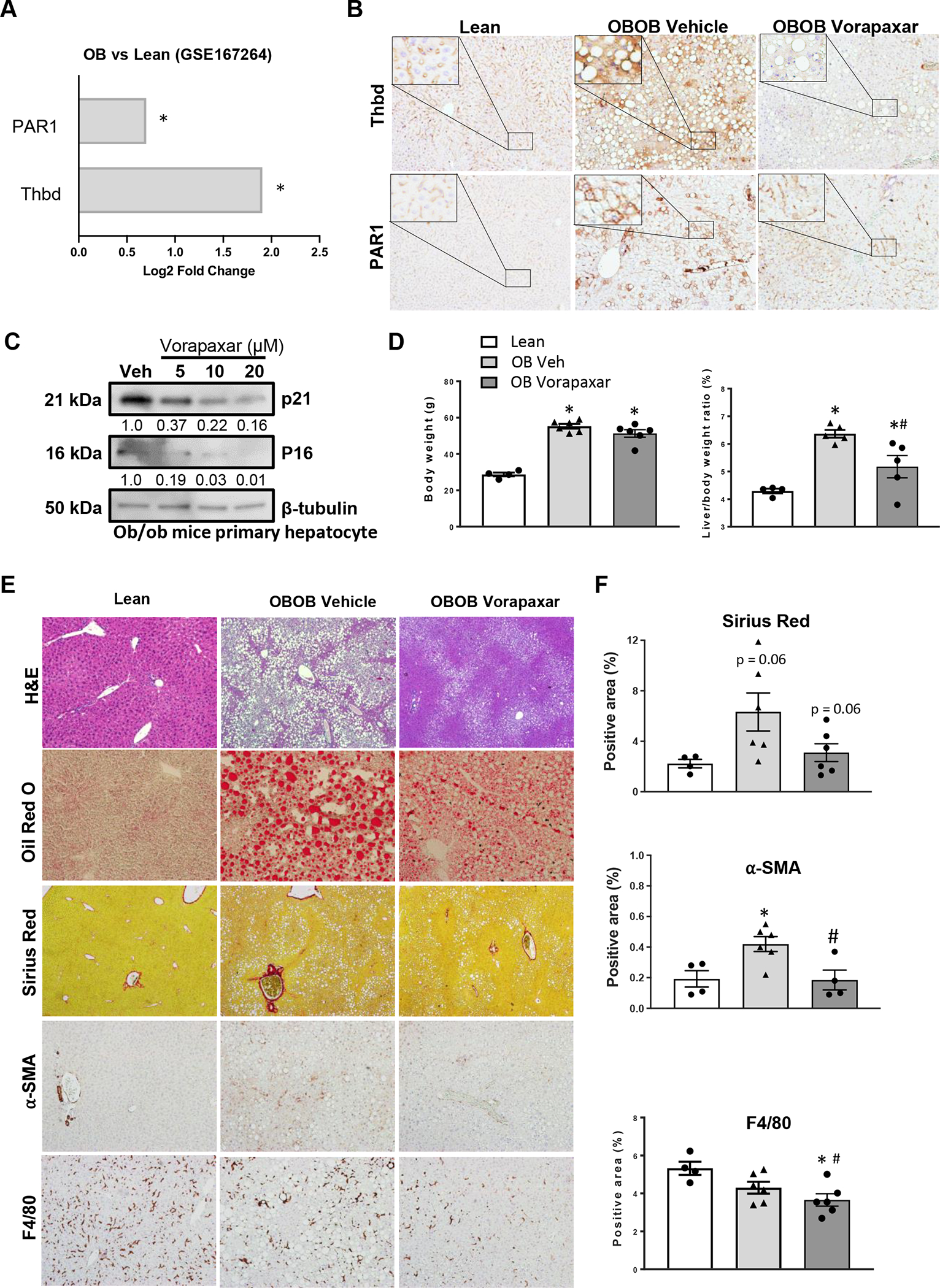
(A) Hepatic expression of THBD and PAR1 was examined in a published RNA-seq dataset (GSE167264), and data graphed as Log2 fold change in obese (ob/ob) vs lean mice *p<0.05. In separate experiments, Vorapaxar or its vehicle control (saline) was administered daily by oral gavage to ob/ob mice for 4 weeks before blood and liver tissue were harvested. Results are compared to age- and sex-matched lean ob/+ littermate controls. (B) Representative photomicrographs of liver sections stained for THBD and PAR1. (C) Dose-dependent effect of vorapaxar on p16 and p21 expression in freshly isolated primary hepatocytes from ob/ob mice. Relative expression of p16 and p21 was normalized to loading control β-tubulin. (D) Body weights and liver/body weight ratios. (E) Liver sections were stained to assess effects of vorapaxar on histology (H&E), fat accumulation (Oil Red O), fibrosis severity (Sirius Red and α-SMA), and inflammation (F4/80 staining). Representative photomicrographs and morphometric quantitation (F). Results shown as MEAN +/− SEM (n=6 mice/group, *p<0.05 vs lean, #p<0.05 vs ob/ob vehicle).
