Figure 4. Suppression of DMN by optogenetic stimulation of anterior insula.
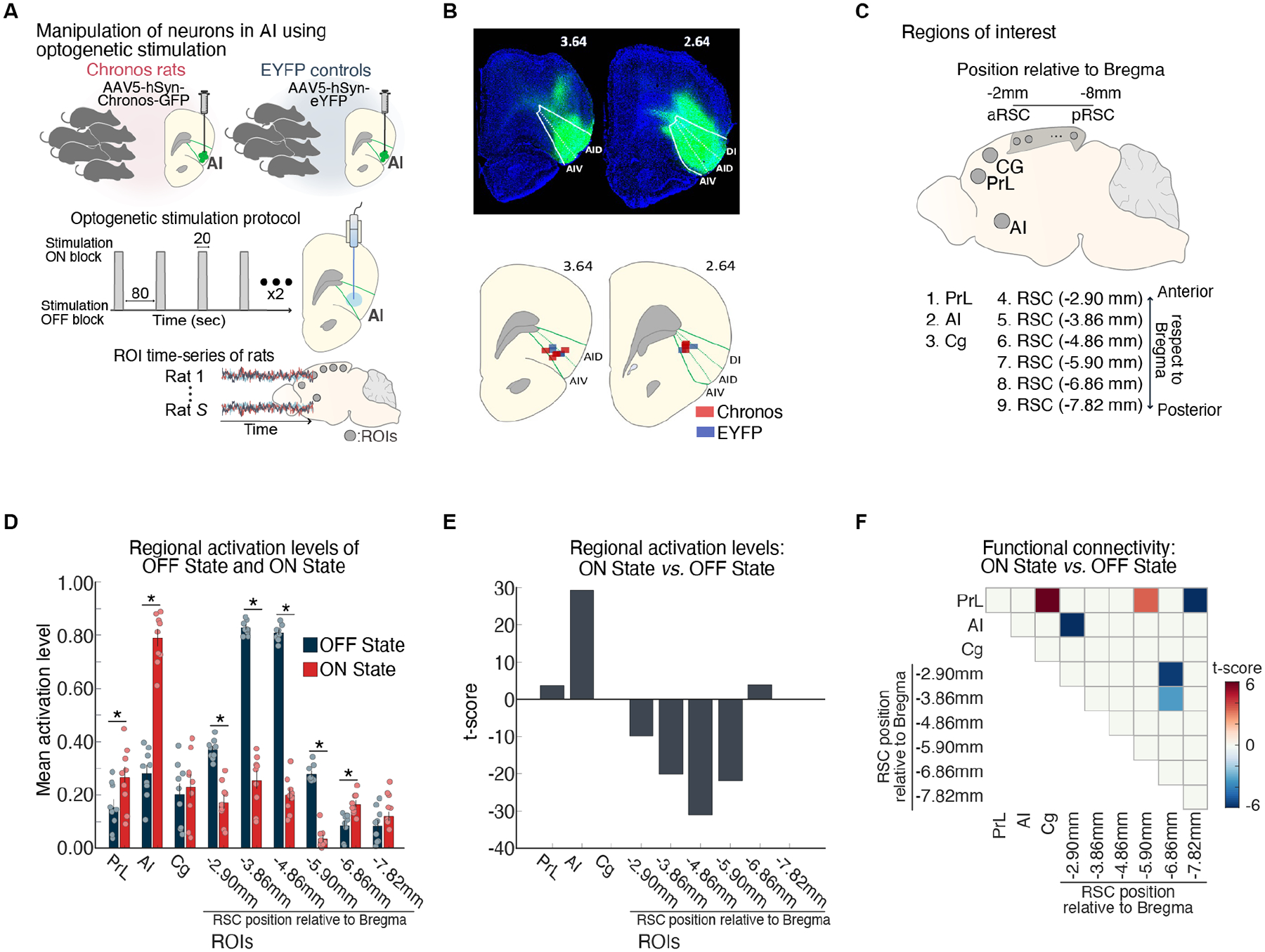
(A) Feedforward optogenetic stimulation of neurons of the right anterior insular (AI) during fMRI in Chronos-expressing rats. Extracted time-series data from ROIs corresponding to putative DMN and salience network nodes. (B) Histological confirmation of EYFP viral vector expression (green) in the dorsal agranular insular cortex (AID), ventral agranular insular cortex (AIV), and dysgranular insular cortex (DI) subdivisions. Optical fiber placement in the AID and AIV subdivisions of the right AI (green). (C) Right AI, cingulate (Cg), prelimbic cortex (PrL), and six subdivisions spanning the anterior-posterior axis of the RSC. (D, E) AI stimulation resulted in activation of AI and PrL and suppression of multiple subdivisions of the RSC nodes of the rodent DMN. (F) Functional connectivity decreased between the AI and an anterior subdivision of the RSC, within the RSC, and between the PrL and a mid-RSC subdivision. Adapted from33; see also34.
