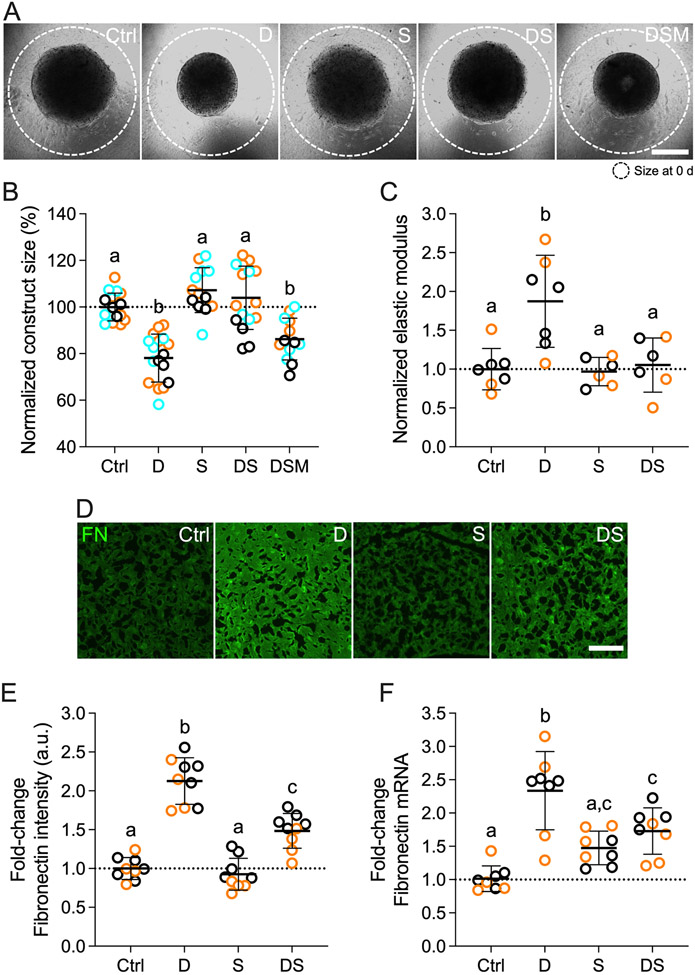
Fig. 4. Effects of simvastatin on HTM hydrogel contraction, stiffness, and FN expression/deposition.
(A) Representative brightfield images of HTM cell-encapsulated ECM hydrogels subjected to vehicle control, dexamethasone (D; 100 nM), simvastatin (S; 10 μM), dexamethasone + simvastatin, and dexamethasone + simvastatin + mevalonate-5-phosphate (M; 500 μM) at 10 d. Dashed lines outline original size of constructs at 0 d. Scale bar, 1 mm. (B) Analysis of HTM hydrogel construct size (N = 13-17 experimental replicates from 3 HTM cell strains). (C) Analysis of HTM hydrogel elastic modulus (N = 6-7 experimental replicates from 2 HTM cell strains). (D) Representative fluorescence micrographs of FN in HTM cell-encapsulated ECM hydrogels. Scale bar, 20 μm. (E) Analysis of FN fluorescence intensity (N = 9 images from 2 HTM cell strains with 2 experimental replicates per cell strain). (F) Analysis of FN mRNA levels (N = 8 experimental replicates from 2 HTM cell strains). Symbols with different colors represent different cell strains; dotted lines indicate control baselines. The bars and error bars indicate Mean ± SD. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA using multiple comparisons tests; shared significance indicator letters = non-significant difference (p>0.05), distinct letters = significant difference (p<0.05).