FIG 4.
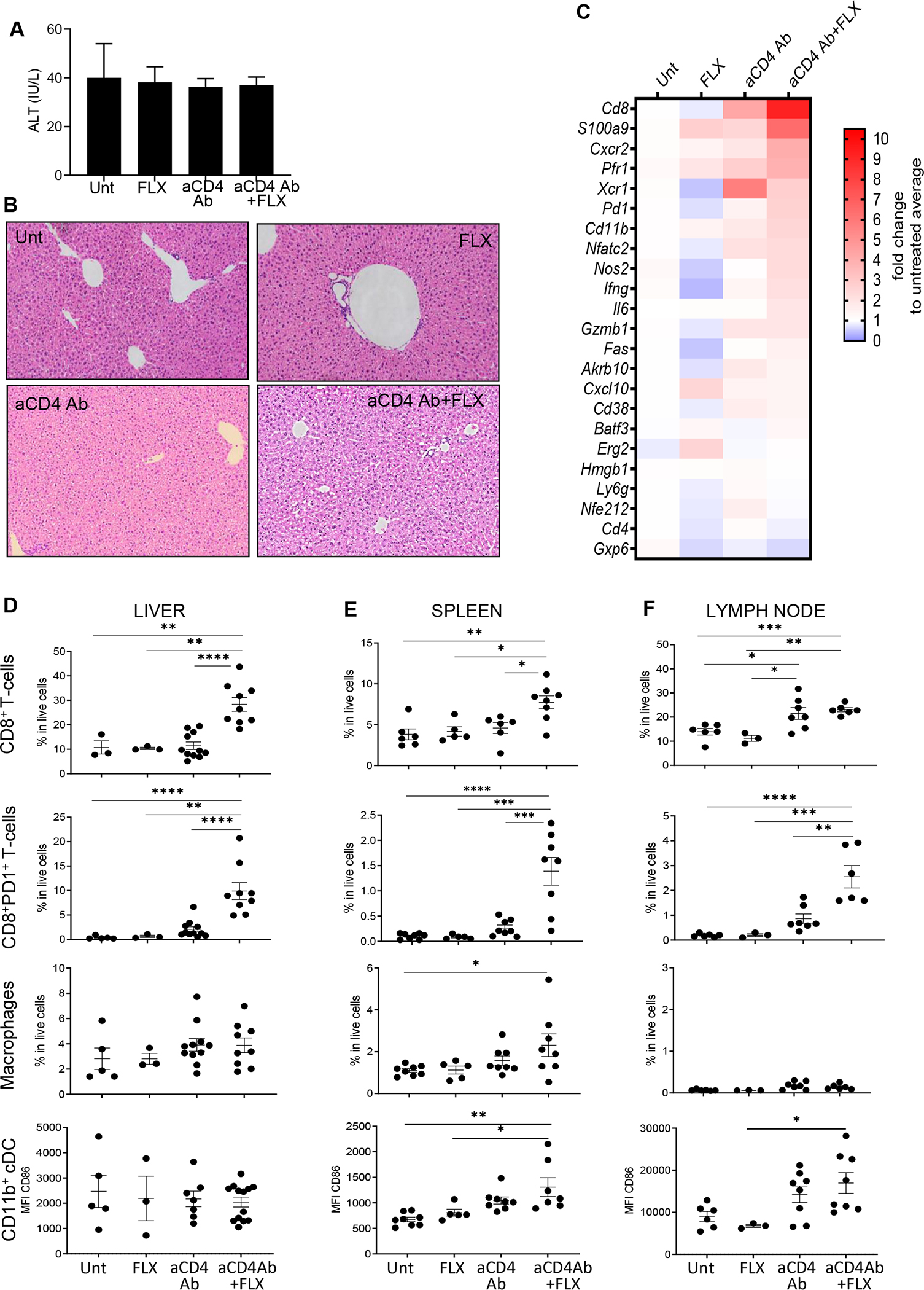
FLX treatment of Tg/KO mice leads to mild liver inflammation if CD4+ T cells, including Treg cells, are depleted. FLX was administered to Tg/KO mice with or without aCD4Ab. All animals were treated with RA. At day 10 after initiation of drug treatment, liver inflammation was evaluated by serum levels of ALTs (A), H&E staining of fixed liver sections (representative mouse per group) (B), and gene expression analysis of perfused liver by real-time PCR (geomean of n = 3–6 mice per group) (C). (D) Infiltrating liver leukocyte populations were isolated from perfused livers and characterized by FACS. Spleen (E) and LN (F) cell suspensions were obtained and analyzed with the same FACS antibody panel (n = 3–9 mice per group). Dead cells were excluded from analysis. Macrophages are CD11bhiF4/80+; cDC CD11b+ are CD19−CD11c+CD8− cells (see gating strategy in Fig E5). *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01, ***P ≤ .001, ****P ≤ .0001, 1-way ANOVA. FACS, Fluorescence-activated cell sorting.
