FIG 5.
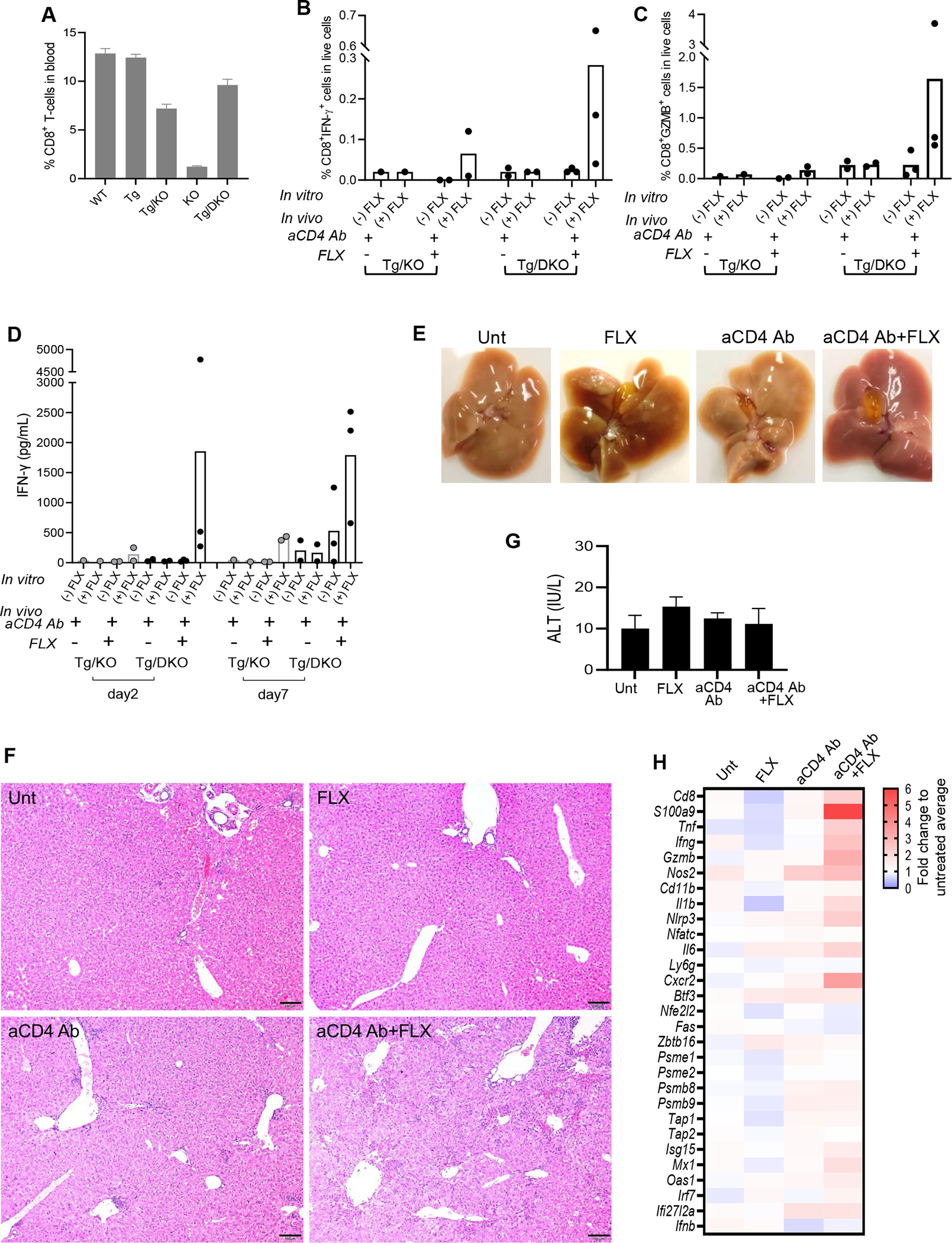
Enhanced drug reaction and liver histopathology in Tg/DKO mice after aCD4Ab + FLX treatment. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of CD8+ T cells in blood of drug-naive animals of different strains. (B-D) Tg/KO or Tg/DKO animals (n = 2–3 per group) were treated with aCD4Ab or aCD4Ab + FLX. Frequency of splenic IFN-γ+CD8+ (B) and GZMB+CD8+ (C) T cells was measured by flow cytometry analysis after day 10 of drug in vivo treatment and subsequent culture in the presence or absence of 250 μg/mL of FLX for 16 hours before adding brefeldin A for 4 hours. (D) IFN-γ levels in culture supernatant of total splenocytes restimulated with or without 250 μg/mL of FLX for 2 or 5 days. (E-H) Tg/DKO mice were treated as described in Methods. (E) Liver and gallbladder at euthanasia (1 representative animal). (F) H&E staining of fixed liver sections (scale bar 5 100 μm) (1 representative mouse per group). Additional sections showed more foci of inflammation in aCD4Ab–treated mice than untreated or FLX control groups, but inflammation and hepatocellular injury were most prominent in the aCD4Ab + FLX group (Fig E4). (G) Serum ALT at day 10 of treatment (n = 3 per group). (H) Gene expression analysis of perfused liver by real-time PCR (geomean of n = 3–12 mice per group).
