FIG 7.
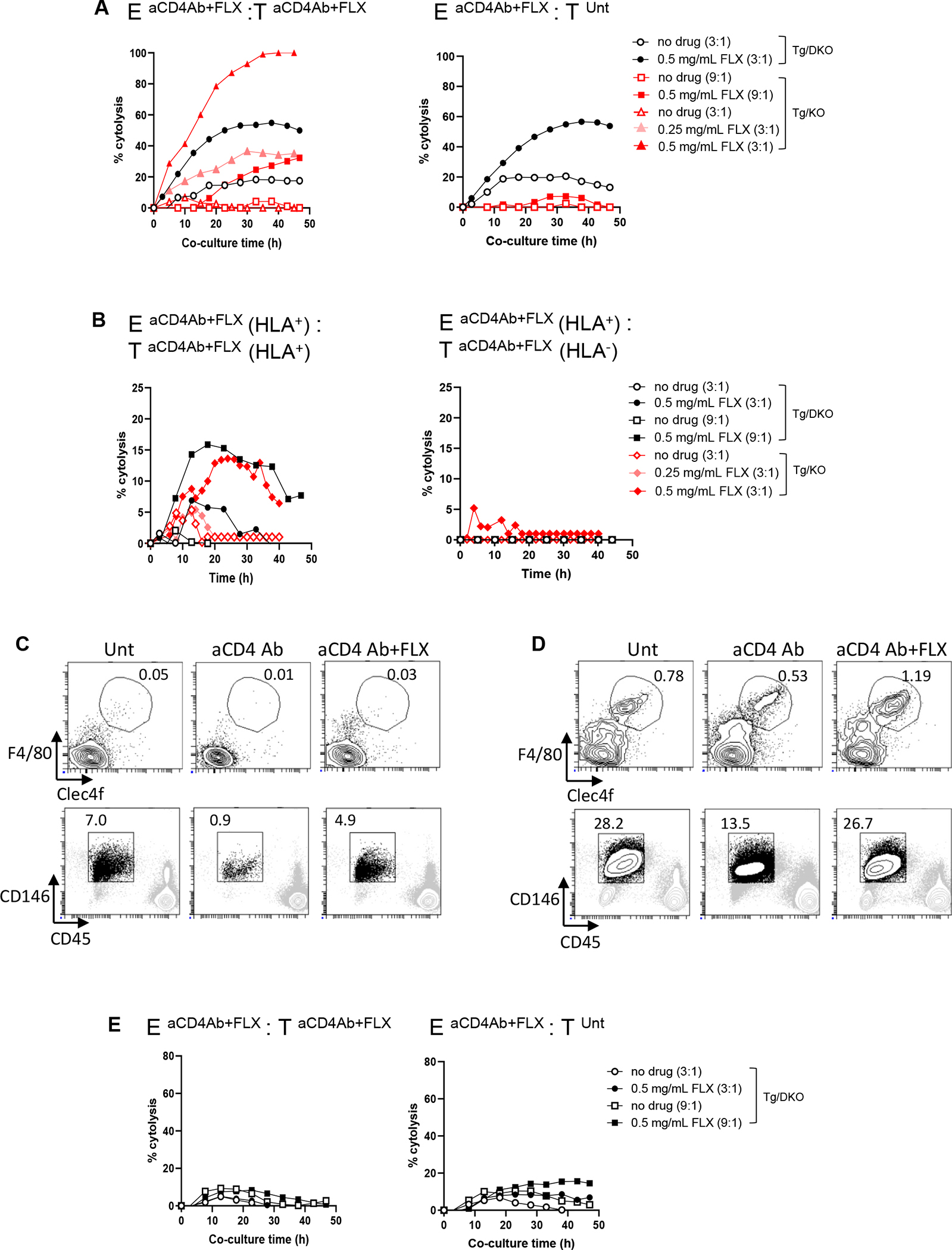
In vitro hepatocyte cytolysis by FLX-reactive leukocytes of mice treated with aCD4Ab + FLX is influenced by drug reexposure, HLA expression, and presence of liver tolerogenic cells. Tg/DKO and Tg/KO animals were treated with aCD4Ab + FLX or left untreated as per our 10-day standard protocol. (A and B) Primary hepatocytes were isolated from perfused livers and seeded in E-plates (target cells [T] at 20,000 cells per well) for 18 hours. Subsequently, liver leukocytes from aCD4Ab + FLX–treated mice (effector cells [E]) were added to cultures at an E:T ratio of 3:1 or 9:1 (E and T from same mouse strain). Superscript annotations correspond to in vivo treatment of animals from which E and T cells were isolated. Selected cocultures were exposed to FLX. Percentage cytolysis was measured as a function of impedance, as indicated in the Methods section in the Online Repository. In (B), T were isolated from HLA+ or HLA− mice from Tg/KO or Tg/DKO strains. E were from HLA+ animals. Different symbols correspond to different animals. (C and D) Frequency of KCs (F4/80+Clec4f+) and LSECs (CD146+CD45−) in cell suspensions of enriched liver leukocytes (C) or bulk NPC (D) from perfused livers of untreated or treated Tg/DKO animals. (E) Cytolysis was evaluated as indicated in (A) but with cocultures of hepatocytes and NPC from perfused livers of Tg/DKO mice.
