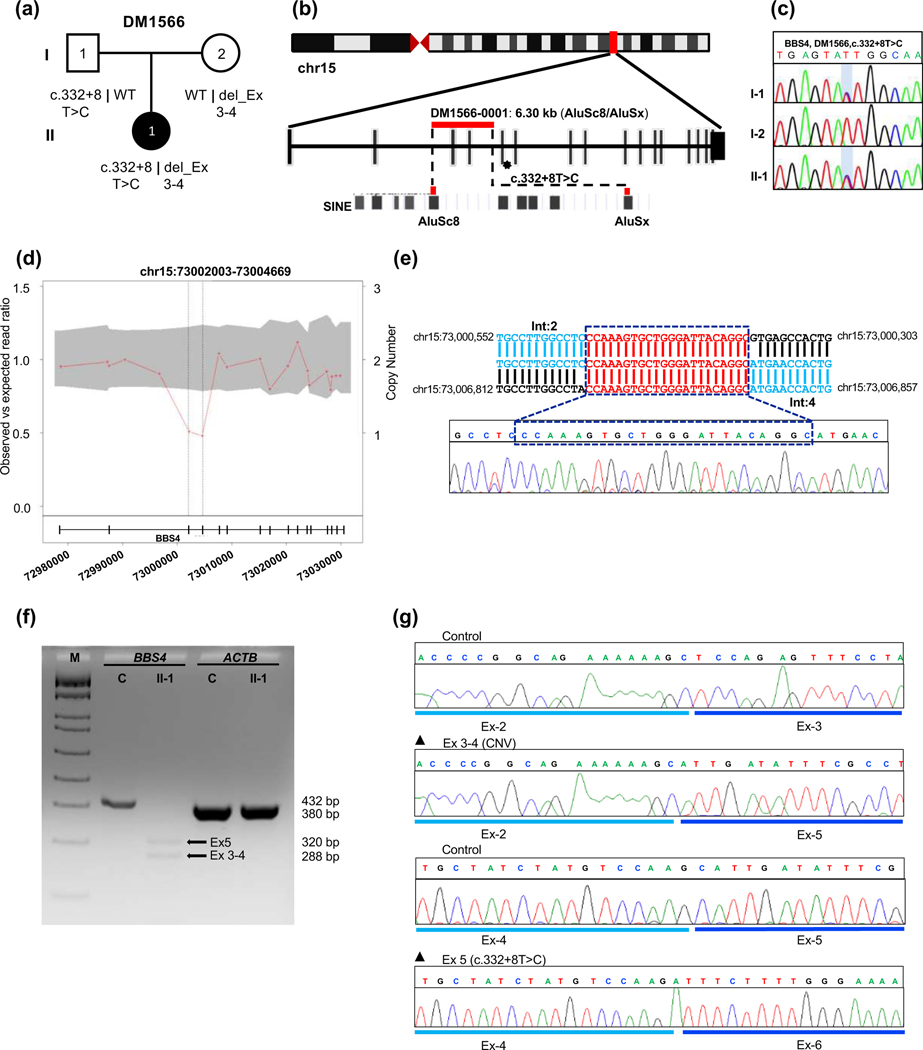
Figure 3. Genetic analysis of DM1566 harboring a biallelic two-exon deletion in trans with a pathogenic splicing variant in BBS4.
(a) Pedigree and segregation analysis of BBS4 variants in DM1566. (b) Schematic representation of human chromosome 15 showing the location of BBS4 with vertical red bar; enlarged view of CNV and SNV bearing region of BBS4 correspond to red horizontal bar and asterisk respectively; AluSc8 and AluSx are indicated at bottom. (c) Sequence chromatogram of paternally-inherited c.332+8T>C change, the variant position is shaded with a light blue vertical bar. (d) CNV plot showing a pathogenic heterozygous two-exon deletions in BBS4, the gray area marks a 95% confidence interval. Black vertical dotted lines indicate the position of the CNV. Bottom, schematic of the BBS4 locus; vertical bars, exons; horizontal line, intronic region; numbers indicate genomic coordinates on chromosome 15 (hg19). (e) BBS4 breakpoint junction sequence in genomic DNA; reference location highlighted in blue and a 22 bp microhomology region present at the junction is shown in red; Int, intron. (f) RT-PCR results show impaired splicing in proband cDNA; 2% agarose gel showing BBS4 amplification products in unaffected control (C, 432 bp expected wild type product) and affected individual II-1 (320 bp band showing exon-5 skipping due to splicing variant and 288 bp band indicating exon 3-4 deletion due to CNV); ACTB (380 bp) was amplified to ensure RNA integrity for both control and proband; M, DNA marker; Ex, exon. (g) Sequence chromatograms of RT-PCR products from unaffected control (top) and DM1566 proband show aberrant mRNA splicing outcomes from maternally inherited exon 3-4 deletion (middle) and paternally inherited exon 5 skipping (bottom).