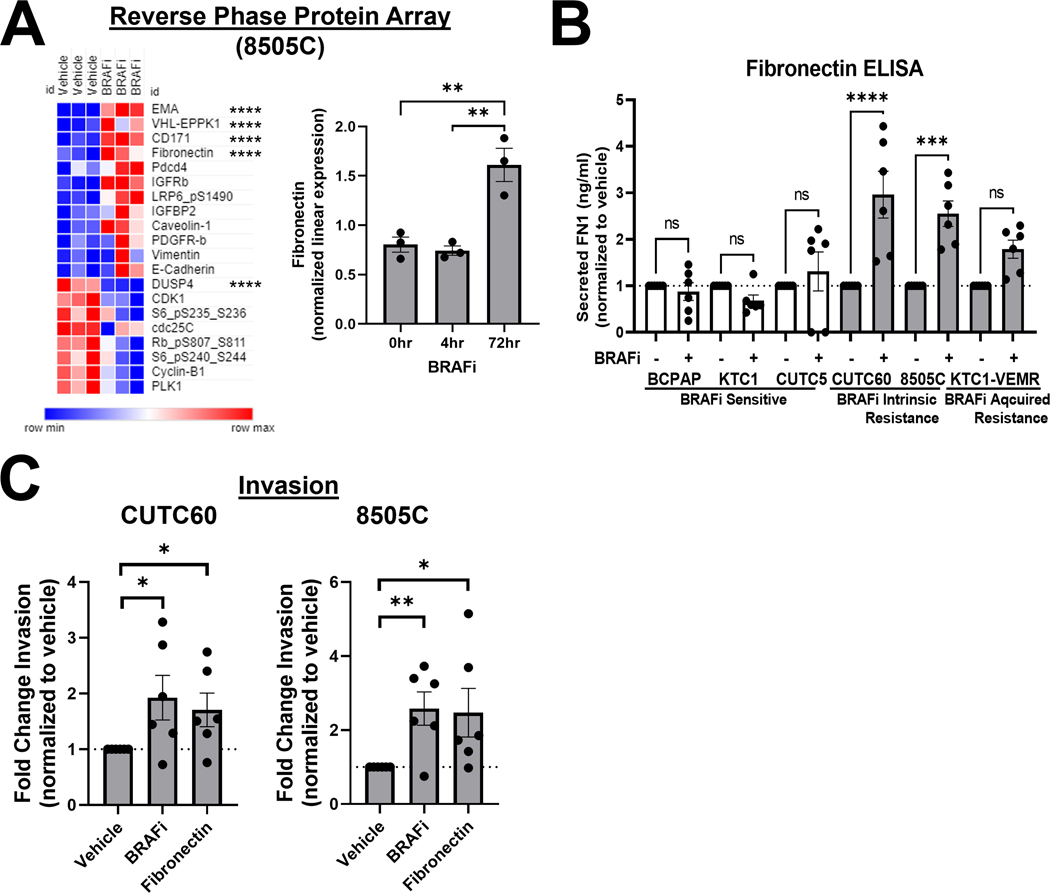
Figure 2. BRAF inhibition increases cellular and secreted fibronectin, which promotes invasion.
A) 8505C cells were treated with 1 μM vemurafenib for 4 or 72 hrs and protein expression was quantified using RPPA (MD Anderson Functional Proteomics Reverse Phase Protein Array Core). Heatmap generated using Morpheus. EMA/MUC1 (epithelial membrane antigen/mucin 1, VHL-EPPK1 (epiplakin 1), CD171 (cell adhesion molecule L1), FN1 (fibronectin), and DUSP4 (dual specificity phosphatase 4) are regulated most significantly. B) Cells were treated with vehicle or BRAFi for 72 hrs and secreted FN1 was quantified using ELISA assays (Invitrogen, Abcam). C) CUTC60 or 8505C cells were treated with either BRAFi or FN1 for 24 hrs, then plated in Matrigel-coated Boyden chambers and allowed to invade for 24 hrs. Invading cells were DAPI stained and quantified using ImageJ or the Cytation 5 Cell Imaging Multi-Mode Reader. Results displayed as mean +/− SEM. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001; ns = not significant. BRAFi: 1 μM vemurafenib or 100 nM dabrafenib, FN1: 100 ng/ml fibronectin.