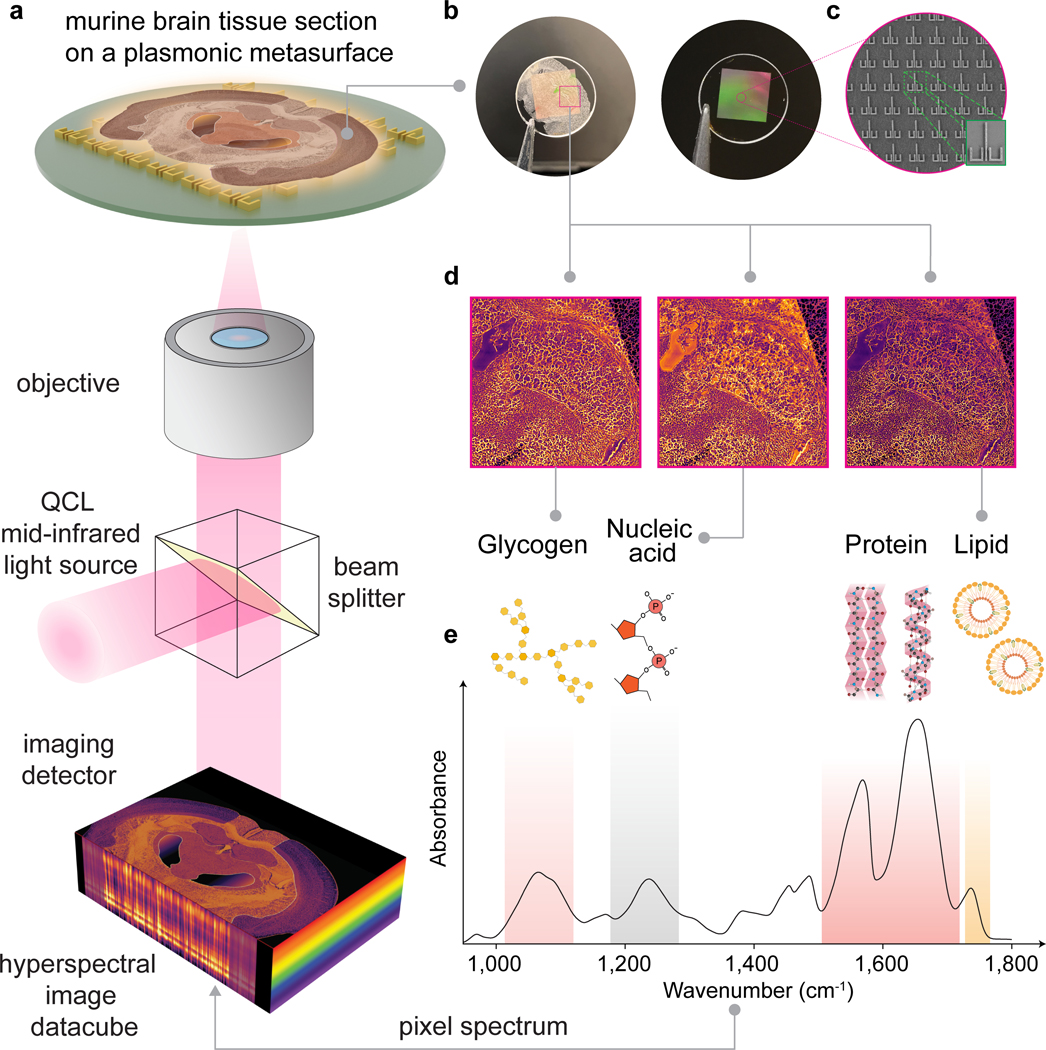
Figure 1 |. Surface-enhanced mid-infrared spectral imaging of tissues (SE-MIRSI).
a, Schematic of the tunable quantum cascade laser (QCL)-based mid-IR spectral imaging system. Hyperspectral datacubes are acquired using a microbolometer focal-plane detector array while sweeping the illumination wavenumber across the mid-IR fingerprint spectral range of 950 to 1,800 cm−1. b, Photographs show a plasmonic metasurface chip fabricated over a 5.5 mm × 5.5 mm area on a CaF2 substrate after and before mounting a murine brain tissue section. c, SEM images show an array of metaunits consisting of ulu-shaped Au nanostructures supporting polarization-multiplexed multi-resonance modes for broadband spectral coverage. d, SE-MIRSI of murine brain tissue section at different wavenumbers corresponding to absorption bands of functional groups present in endogenous biomolecules such as glycogens, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids. e, A characteristic mid-IR absorption spectrum of mouse brain tissue.