Figure 7: Both extracellular loops in the MARVEL domain in CMTM6 are required for binding of CD58 or PD-L1.
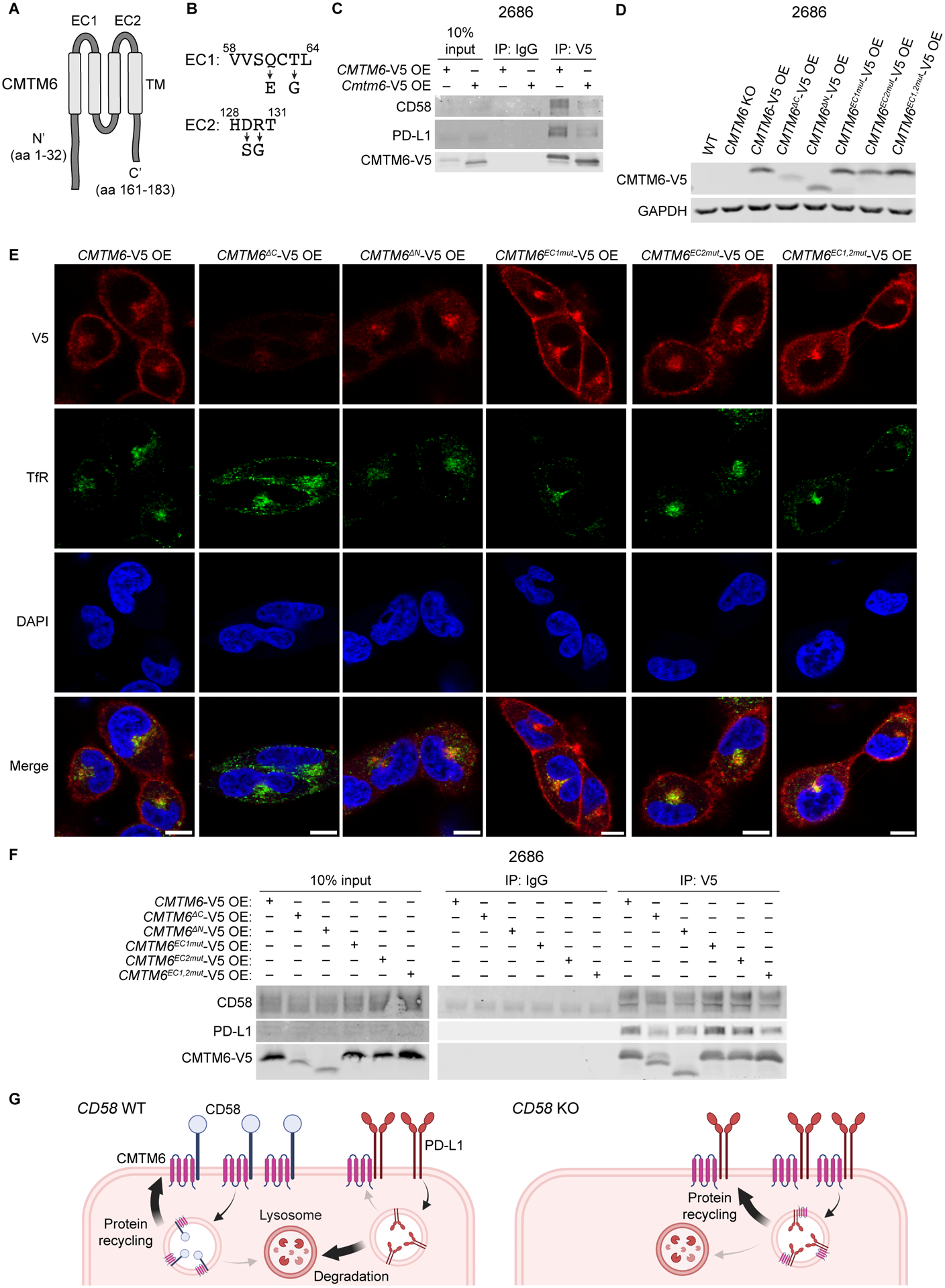
(A) AlphaFold prediction for human CMTM6 protein structure includes transmembrane (TM) MARVEL domain, two extracellular (EC) loops, and intracellular N’ and C’ tails50,51.
(B) Altered amino acid sequences within extracellular loops of CMTM6 for EC1 and EC2 mutants derived from homologous regions in murine CMTM6.
(C) Co-IP of PD-L1 and CD58 with human or mouse CMTM6 using anti-V5 IP in 2686 CMTM6-V5 OE and Cmtm6-V5 OE cells after 72h with 10 ng/mL IFN-ɣ.
(D) Immunoblotting for V5-tagged protein in 2686 WT, CMTM6 KO, CMTM6-V5 OE, and shown CMTM6 mutant, V5-tagged protein-expressing cells.
(E) 2686 V5-tagged CMTM6 WT and mutant-expressing cells were fixed and stained for V5 and transferrin receptor (TfR) and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Scale bars = 10 μm.
(F) Co-IP of PD-L1 and CD58 with V5-tagged protein in 2686 V5-tagged CMTM6 WT and mutant-expressing cells after 72h with 10 ng/mL IFN-ɣ.
(G) Proposed model of PD-L1 regulation by CD58.
Representative images shown from two independent experiments (C, E, F).
