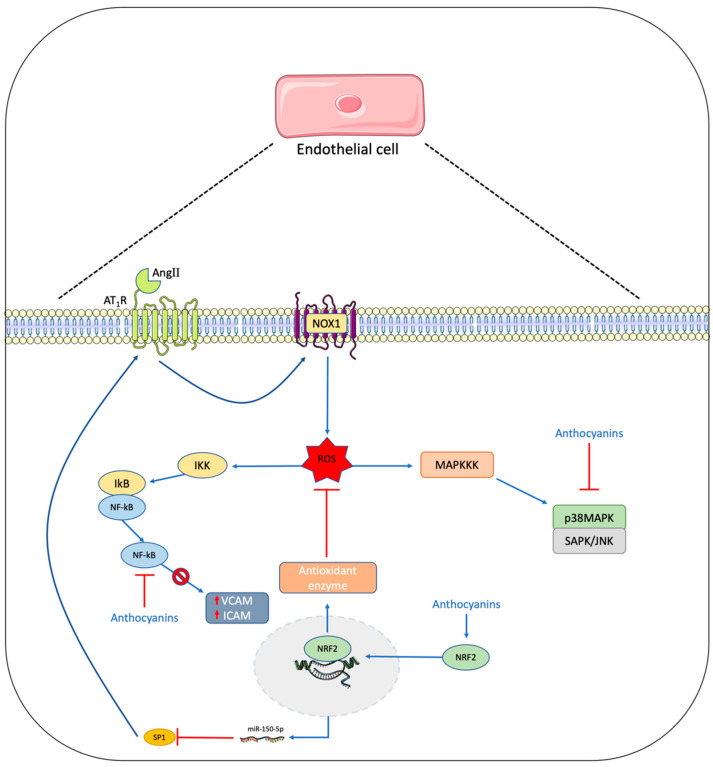
Figure 3.
The main mechanisms through which anthocyanins can influence the expression of proinflammatory and antioxidant proteins. Anthocyanins can block NF-κB, reducing the expression of VCAM and ICAM proteins, and can meanwhile activate NRF2-inducing antioxidant enzyme production and regulate miR-150 levels. Abbreviations: ATR (angiotensin II type-I receptor), AngII (angiotensin II), ICAM (intercellular adhesion molecule-1), IKB (inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappa B), IKK (IKB kinase), JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinases), MAPKKK (MAPK kinase kinase), NF-κB (nuclear factor-kappa B), NOX1 (NADPH oxidase 1), NRF2 (nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2), p38MAPK (MAP-kinase p38), ROS (reactive oxygen species), SAPK (stress-activated protein kinases), SP1 (specific protein 1), VCAM (vascular cell adhesion protein-1).