Table 1.
Examples of natural antioxidants candidates for improving clinical outcomes in patients undergoing MIRI and/or cerebral IRI.
| Antioxidant Family | Antioxidant | Formula | Prevention Proposed | Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyphenols | Resveratrol |
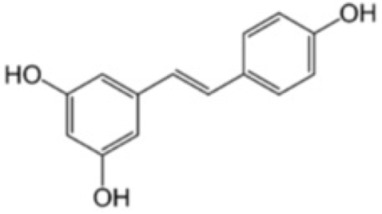
|
MIRI [60] and CIRI [61] | Ameliorate OS by increase in Nrf2 expression [61,62]. Also, decrease inflammation through TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway [61,63]. |
| Quercetin |
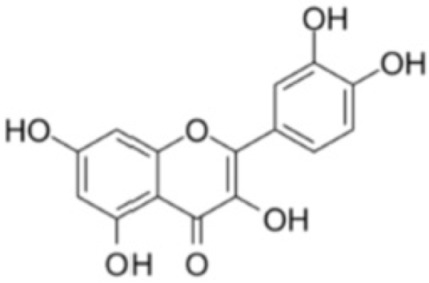
|
MIRI [64] and CIRI [65,66] |
Scavenging and inhibition of ROS, and induction of Nrf2/HO-1 expression [65]. | |
| Curcumin |
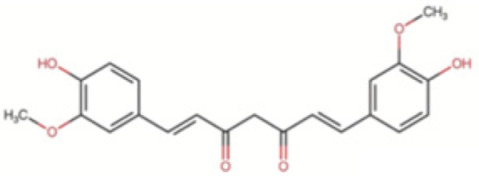
|
MIRI [67] and CIRI [68] | Decrease myocardial apoptosis by activating JAK2/STAT3 pathway, thus reducing OS-damage [67]; while neuroprotection could be due to inhibition of pyroptosis by suppressing the p38 MAPK pathway [69]. | |
| Carotenoids | Lycopene |
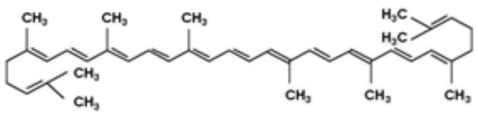
|
MIRI [33] and CIRI [70] | Inhibit mPTP opening via modulation of Bax and Bcl-2 [33,70]. |
| Crocin |
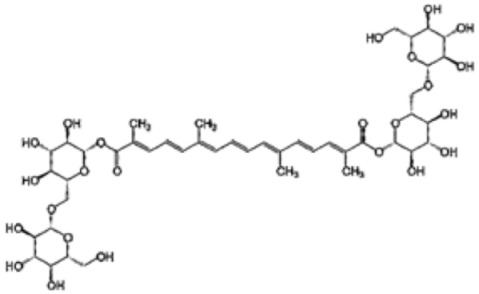
|
MIRI [71] and CIRI [58] | In the heart, there is a regulation of SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling and related endoplasmic reticulum stress [71], while in the brain, a reduction in HIF-1α and caspase-3 was seen [58]. | |
| β-carotene |
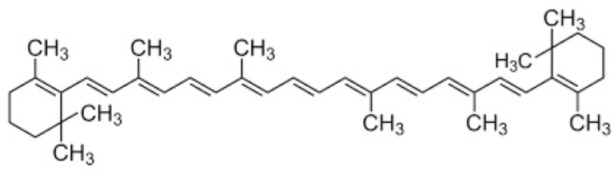
|
MIRI [72] and CIRI [73] | Inhibit NF-κB pathway [73]. | |
| Astaxanthin |
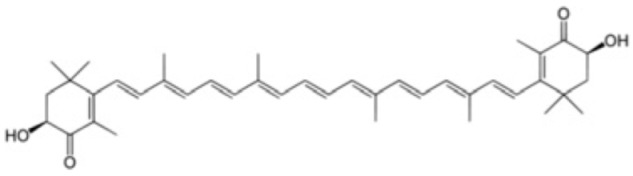
|
MIRI [74] and CIRI [75] | Activate Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, regulate the miR-138/HIF-1α axis [74]. Enhance the expressions of SOD1 and 2 [75] | |
| Lutein |
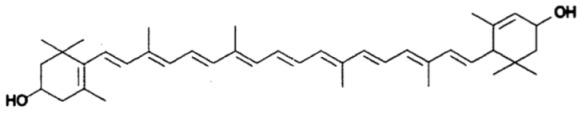
|
CIRI [76] | Decrease SOD, CAT and GTX activity [76]. | |
| Vitamins | All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) |
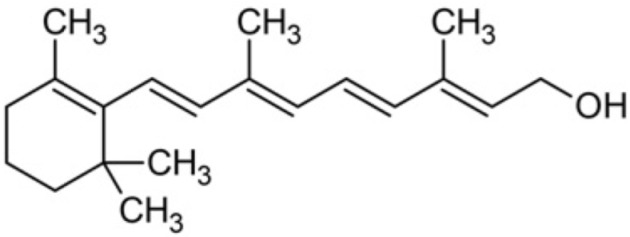
|
MIRI [77] and CIRI [78] | Downregulation of MAPK signaling [77,78]. |
| Vitamin C |
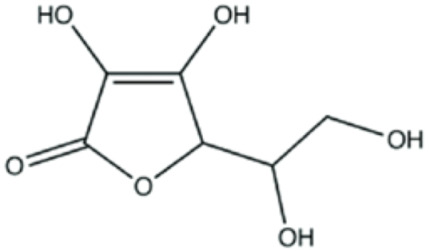
|
MIRI [79] and CIRI [80] |
Decrease SOD activity [81] and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway [79]. | |
| Vitamin D (α-tocopherol) |
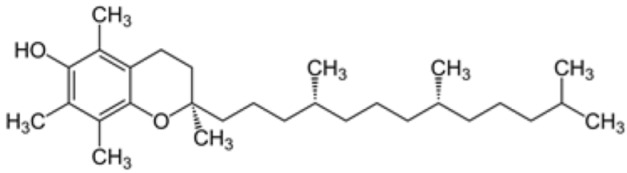
|
MIRI [82] and CIRI [83] | Reduce inflammation RhoA/ROCK/NF-ĸB pathway [82], activate Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, and suppress NLRP3-mediated pyroptotic pathway [83]. | |
| Vitamin E |
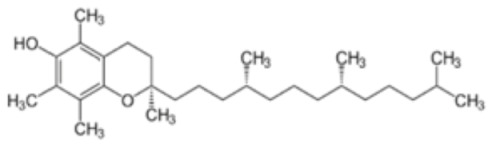
|
MIRI [84] and CIRI [85] | Downregulation of GPX (1, 5 and 6) and MPO [84]. | |
| Folic acid |
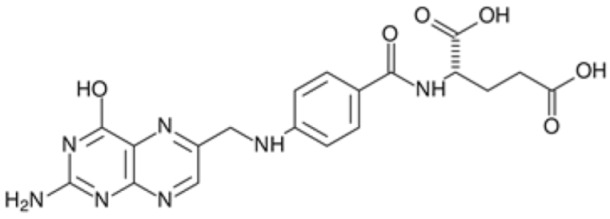
|
CIRI [86] | Inhibition of NMDAR [86]. | |
| Others | Ginsenoside Rg1 |
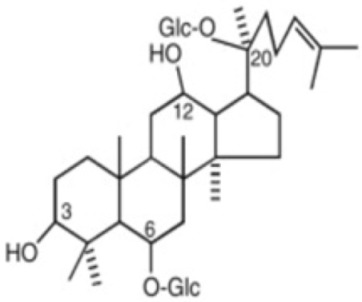
|
CIRI [87] | Activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway [88]. |
| Ginsenoside Rb1 |
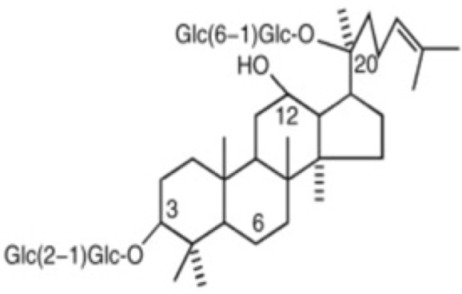
|
MIRI [89,90] | Reduce succinate-driven ROS production by inhibiting NADH dehydrogenase in mitochondrial complex I [91]. |
Akt: protein kinase B; ARE: antioxidant response elements; CIRI: cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury; GPX: glutathione peroxidase; HO-1: heme oxygenase-1; MIRI: myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury; MPO: myeloperoxidase; mPTP: mitochondrial permeability transition pore; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SIRT1: sirtuin 1; SOD: superoxide dismutase; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4.
