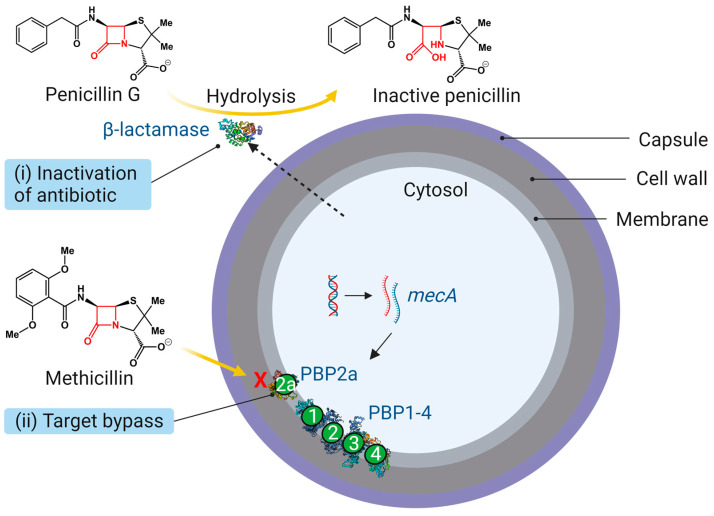
Figure 3.
Molecular mechanisms of β-lactam resistance in S. aureus. (i) Inactivation of antibiotic: hydrolysis of the amide bond of penicillin G by β-lactamase, rendering the antibiotic inactive [7]. (ii) Target bypass: the TPase activity of PBP2 targeted by β-lactams is taken over by acquired PBP2a in MRSA, which is not inhibited by β-lactams [12].