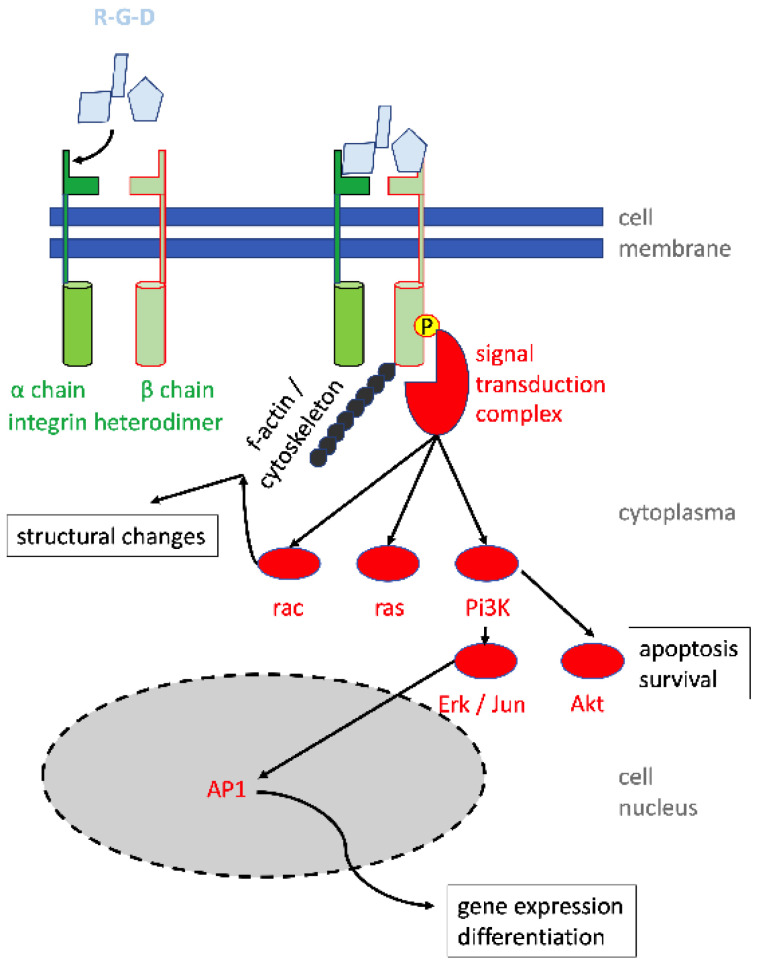
Figure 4.
Integrin signaling and regulation of structural changes, cell survival, differentiation, and gene expression. Peptides (light blue) bind first to the integrin α chain, causing a conformational change, thus facilitating an approximation to the integrin β chain. A high-affinity integrin complex is generated (green), and both cytoskeletal components (e.g., f-actin; black) as well signal transduction proteins (e.g., vinculin, paxillin, talin, focal adhesion kinase; red) bind to the intracellular domain of the integrin β chain. Secondary intracellular signal pathways include rac, ras, pi3K, erk, akt, and others. They relay signals, for instance to AP1 binding sites in integrin-regulated promotor sequences.