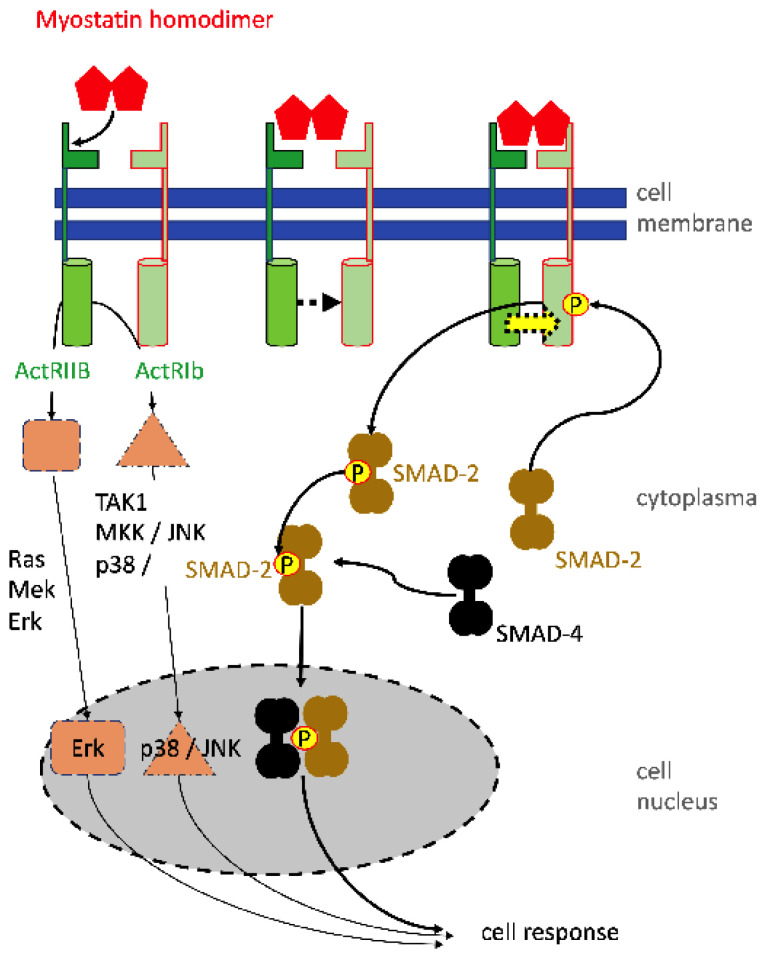
Figure 5.
Myostatin-dependent cell signaling involves SMAD and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways. Myostatin id, a member of the TGF-beta family, therefore uses basically the same signal transduction pathways (compare Figure 1). A significant difference to other members of the TGF family of cytokines is that myostatin inhibits proliferation and differentiation of myogenic progenitor cells. In addition to the classical SMAD-dependent signaling, myostatin binding to the Act receptor II B induces activation of two kinase pathways relaying signals via Ras–Mek-Erk1/2 and Tak1–Mkk to p38MAP kinases or through Jnk. Erk, p38MAP kinase, and Jnk interact in the cell nucleus with transcription factors and there modulate the expression of myostatin target genes.