Figure 1. Spock1 induces BBB functional development.
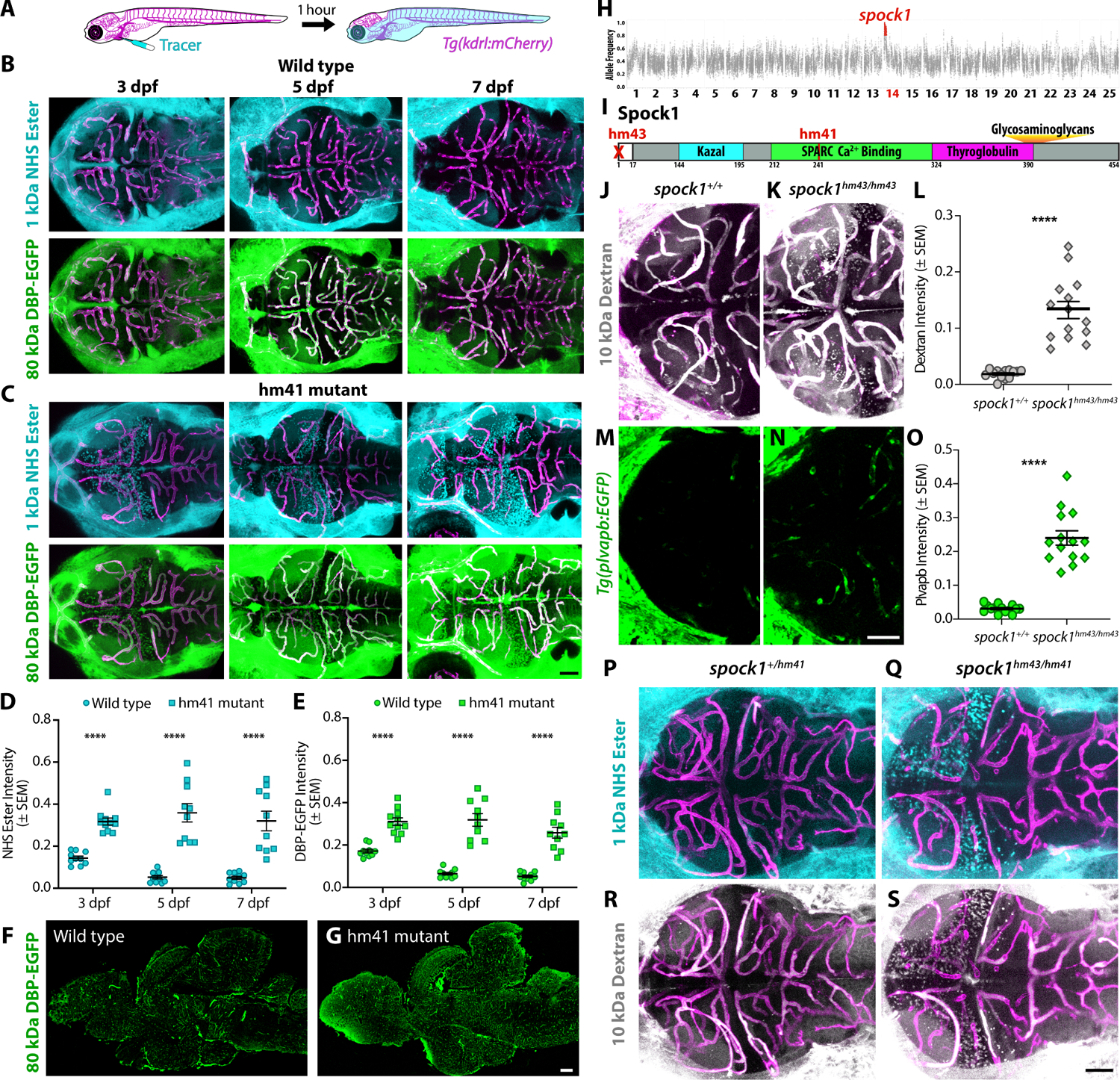
(A-E) Fluorescent tracer leakage assays in larval zebrafish reveal BBB leakage in the forebrain and midbrain of both injected 1 kDa Alexa Fluor 405 NHS Ester (turquoise) and 80 kDa DBP-EGFP (green) of hm41 homozygous larvae (C) compared to wild type controls (B) throughout larval development, as quantified in D and E. (F-G) Sagittal sections of adult brains show that the mutant leakage persists into adulthood (G). (H) Linkage mapping of the hm41 mutant phenotype reveals tight linkage to spock1 on chromosome 14. (I) Spock1hm41 has several point mutations (T241A and several silent mutations) in the SPARC domain. Spock1hm43 has a deletion of the 5’ UTR and start codon. (J-O) Dextran leakage assays show spock1hm43/hm43 mutants (K) have increased BBB leakage (L). spock1hm43/hm43 mutants also have increased expression of the leaky vessel marker plvapb (N and O). (P-S) Compound spock1hm43/hm41 heterozygotes also display increased NHS Ester (Q) and Dextran (S) leakage compared to spock1hm41/+ heterozygote siblings, which confine both injected tracers at 5 dpf (P and R). Scale bars represent 50 μm (C, N, S) and 200 μm (G). N = 10 (D and E) and 14 (L and O), with each point representing an individual fish. **** p<0.0001 by 2way ANOVA (D and E) and by t test (L and O).
