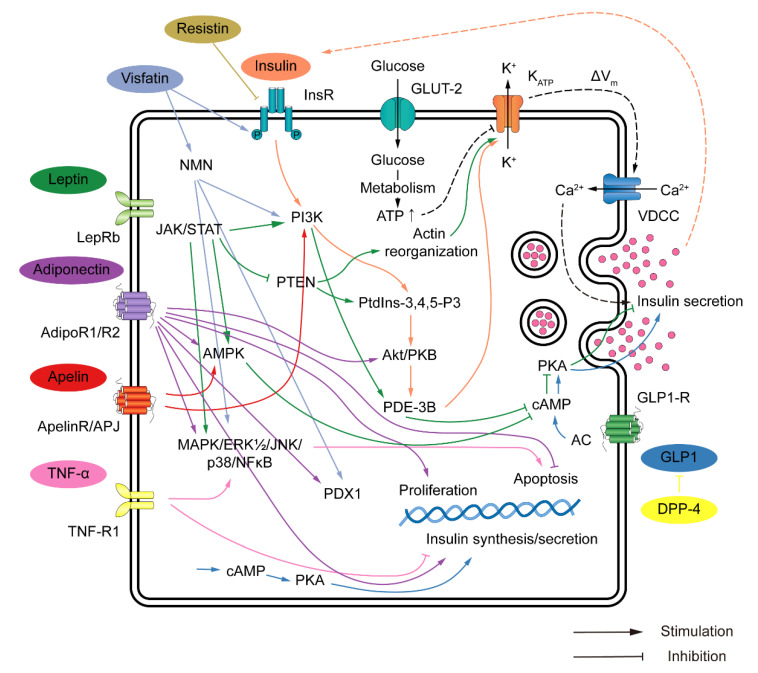
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the role of adipokines in pancreatic beta cells. AdipoR, adiponectin receptor; Akt/PKB, protein kinase B; AMPK, 5′ AMP-activated protein kinase; ApelinR, apelin receptor; DPP-4, dipeptidylpeptidase-4; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; GLUT-2, glucose transporter 2; GLP1, glucagon-like peptide-1; InsR, insulin receptor; JAK/STAT, Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases; KATP, ATP-sensitive potassium channel; LepRb, leptin receptor long isoform; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; PDE-3B, phosphodiesterase 3B; PDX-1, pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase; PtdIns-3,4,5-P3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; VDCC, voltage-gated calcium channel.