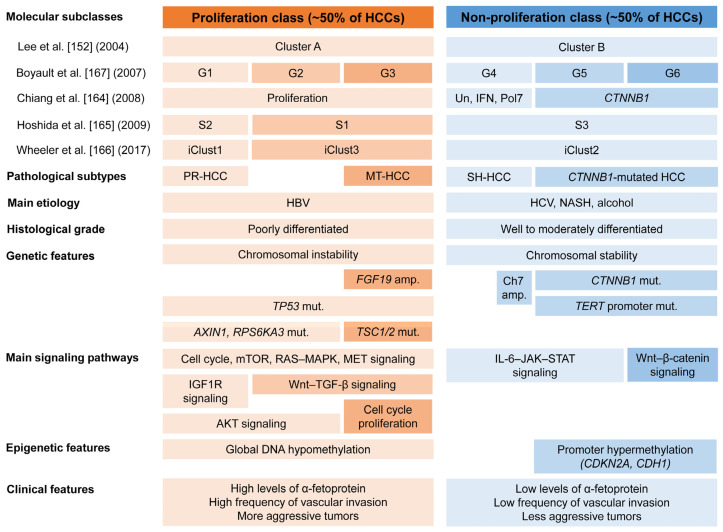
Figure 7.
Molecular classes and subclasses of hepatocellular carcinoma. HCCs are classified into two major molecular classes: the proliferation and non-proliferation class. For each molecular subclass, pathological subtypes, main etiology, histological grade, main signaling pathway, genetic, epigenetic, and clinical features are displayed. Macrotrabecular massive HCC is assigned to the G3 subgroup. Progenitor HCC is associated with the S2 or iClust1 subgroup. A subset of HCC within the G4 subgroup frequently exhibits ST-HCC subtype. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; Un, unannotated class; IFN, interferon-related class; Pol7, class defined by polysomy of chromosome 7; iClust, integrated cluster; PR-HCC, progenitor HCC; MT-HCC, macrotrabecular massive HCC; SH-HCC, steatohepatitic HCC; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; amp., amplification; Ch7, chromosome 7; mut., mutation; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MET, mesenchymal–epithelial transition; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; AKT, Ak strain transforming; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; IL-6, interleukin-6; JAK, Janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription [135,164,165,166,167].