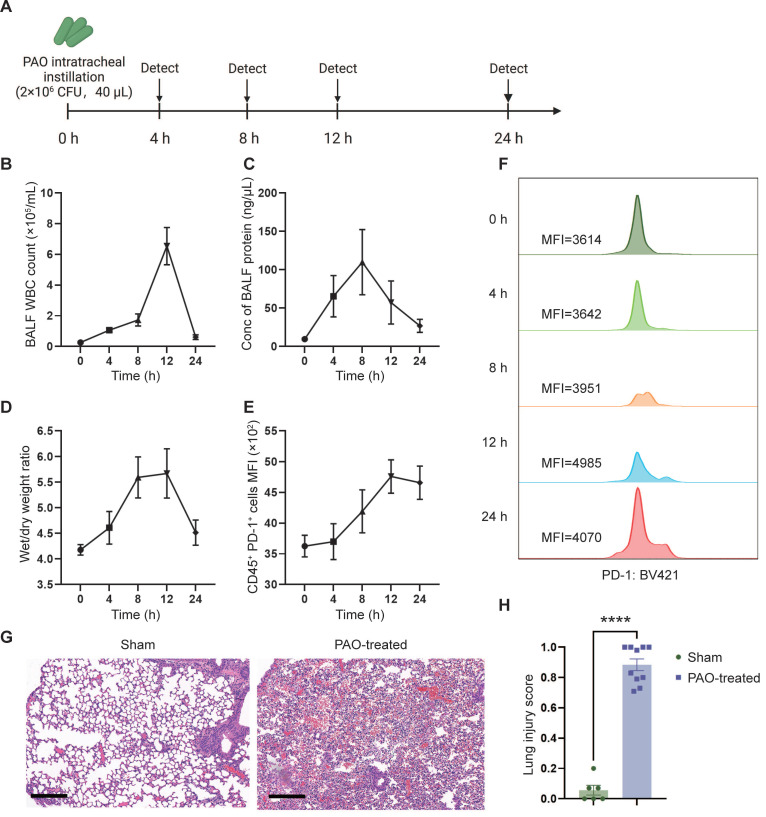
Figure 4.
PAO-induced ARDS mouse models. ARDS mice were modeled by pouring PAO bacterial solution into the lungs by endotracheal intubation (2×106 CFU/mL, 40 µL/mouse). ARDS mice were sacrificed at different time points (0 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, 24 h) after modeling and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and partial lung tissue were collected for testing. (A) Schematic depicting the experiment workflow. (B) Time course of the white blood cell (WBC) count in the BALF. WBC were counted by Cell Count. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 5). (C) Time course of the concentration of BALF protein. Concentration of protein was determined by Bradford method. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 5). (D) Time course of wet/dry weight ratio of the right upper lobe of the lung. Wet weight of the tissues was weighed immediately and dry weight data were collected after 48 hours of drying. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 3). (E) Time course of changes in PD-1 expression in lung immune cells (CD45+) over time. PD-1 was stained with BV421-CD279 antibody and CD45 was stained APC-CD45 antibody. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 5). MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. (F) Histogram of PD-1 MFI at different time points. (G) Representative pathology of normal lung (left) and ARDS lung (right, at 12-hour time point). Scale bar, 200 μm. (H) Lung injury scoring comparison between groups with or without PAO treatment (n = 5). ****p < 0.0001.