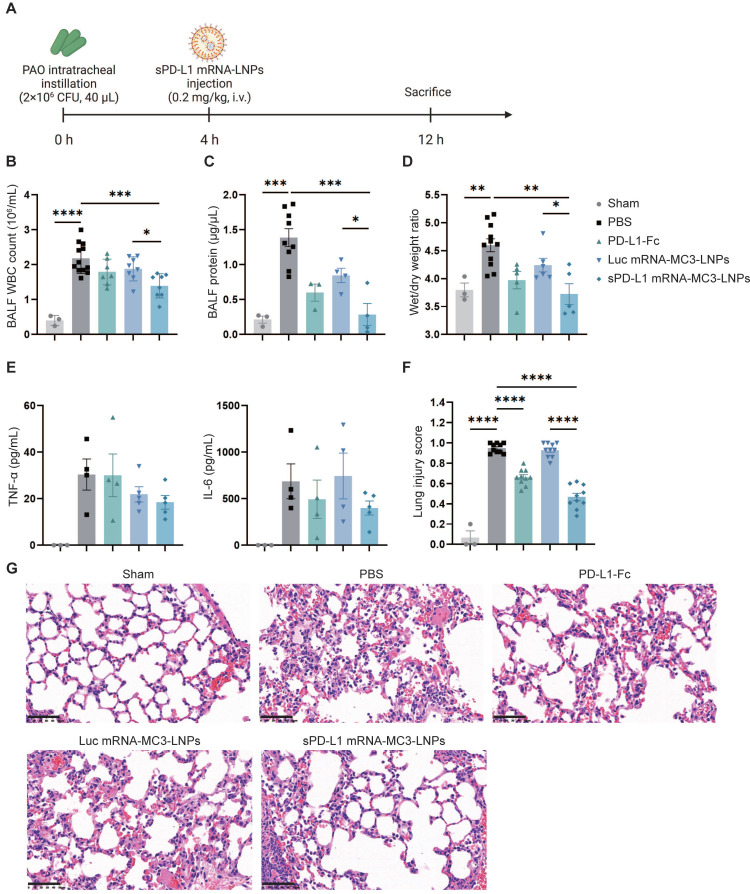
Figure 5.
In vivo therapeutic effect of sPD-L1 mRNA-MC3-LNPs. (A) Schematic depicting the experiment workflow. ARDS mice were modeled by pouring PAO bacterial solution into the lungs by endotracheal intubation (2×106 CFU/mL, 40 µL/mouse). Four hours later, mice received a tail vein administration (PBS, 0.8 mg/kg PD-L1-Fc, 0.2 mg/kg Luc mRNA-MC3-LNPs, 0.2 mg/kg sPD-L1 mRNA-DOTAP-LNPs) (n = 3-12). After 12 hours, mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. Then BALF and partial lung tissue were collected for testing. Sham, use PBS solution to model. (A) Schematic depicting the experiment workflow. (B) WBC count in the BALF. WBC were counted by Cell Count. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 3-12). (C) Protein concentration in the BALF. Concentration of protein was determined by Bradford methods. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 3-9). (D) Wet/dry weight ratio of the right upper lobe. Wet weight of the tissue was weighed immediately and dry weight data were collected after 48 hours of drying. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 3-11). (E) Concentration of inflammatory factor (TNF-α, IL-6) in the BALF. ELISA was used to determine the concentrations of the inflammatory cytokines. Results represent mean ± SEM (n = 3-5). (F) Lung injury scoring of HE stained sections (n = 3-5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. t-test analysis. (G) Representative pathology of ARDS lungs treated with different drugs (Sham, PBS, PD-L1-Fc, Luc mRNA-MC3-LNPs, sPD-L1 mRNA-MC3-LNPs, at 12-hour time point). Scale bar, 50 μm.