Figure 3. The renin cell baroreceptor is a nuclear mechanotransducer.
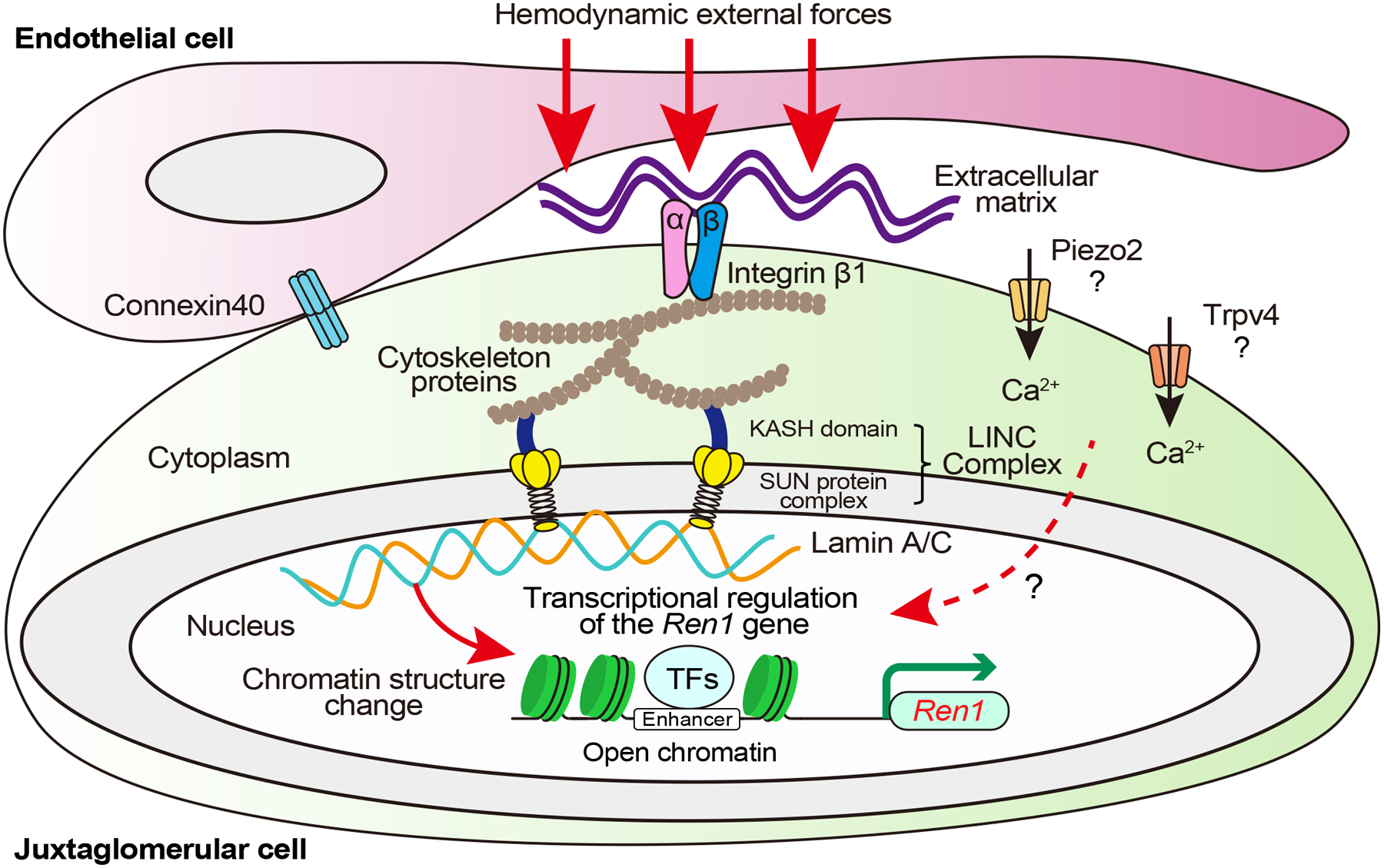
Hemodynamic external forces are sensed by integrins and transmitted through the cytoskeleton likely to the linker of the nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex, ultimately impacting lamina-chromatin interactions that change chromatin structure and upregulate Ren1 gene transcription in response to low perfusion pressure and downregulates Ren1 in response to high perfusion pressure. Connexins in renin cells and endothelial cells determine the position around afferent arterioles where the renin cells can adequately sense hemodynamic external forces. Whether mechanically activated non-voltage-gated calcium-permeable ion channels, such as Piezo2 and transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (Trpv4), regulate intracellular calcium and renin release in juxtaglomerular cells remains to be determined. KASH, Klarsicht/ANC-1/Syne-1 homology; SUN, Sad1/UNC-84 homology.
